Municipal water distribution planning plays a crucial role when it comes to sustainable infrastructure development. It involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure the efficient and effective supply of clean water to the community. The key considerations for sustainable infrastructure development in municipal water distribution planning will be explored in this article.
Population Growth and Demand
One of the primary considerations in municipal water distribution planning is the population growth and demand for water. As a city’s population increases, the water demand also rises. It is essential to assess the current and projected future population growth to determine the required infrastructure capacity. This includes evaluating the existing water sources, treatment plants and distribution networks to meet the growing demand.
Water Source and Quality
The availability and quality of the water source are critical factors in sustainable infrastructure development. Municipalities need to identify reliable water sources that can meet the demand while ensuring the water quality meets the required standards. This may involve exploring alternative sources, such as groundwater or surface water, and implementing appropriate treatment processes to ensure the water is safe for consumption.
Distribution Network Design
The design of the distribution network is another key consideration in municipal water distribution planning. It involves determining the optimal layout of pipes, valves and storage facilities to ensure efficient water flow and pressure throughout the system. Factors such as distance, elevation and hydraulic modeling are taken into account to minimize water loss and maximize distribution efficiency.
Infrastructure Maintenance and Upgrades
Maintaining and upgrading the existing infrastructure is crucial for sustainable water distribution planning. Regular inspections, repairs and replacements from a team of experienced professionals like A & V Water, are necessary to prevent leaks, reduce water loss and ensure the longevity of the system. Additionally, as technology advances, municipalities should consider incorporating smart infrastructure solutions that enable real-time monitoring and efficient management of the distribution network.
Environmental Impact
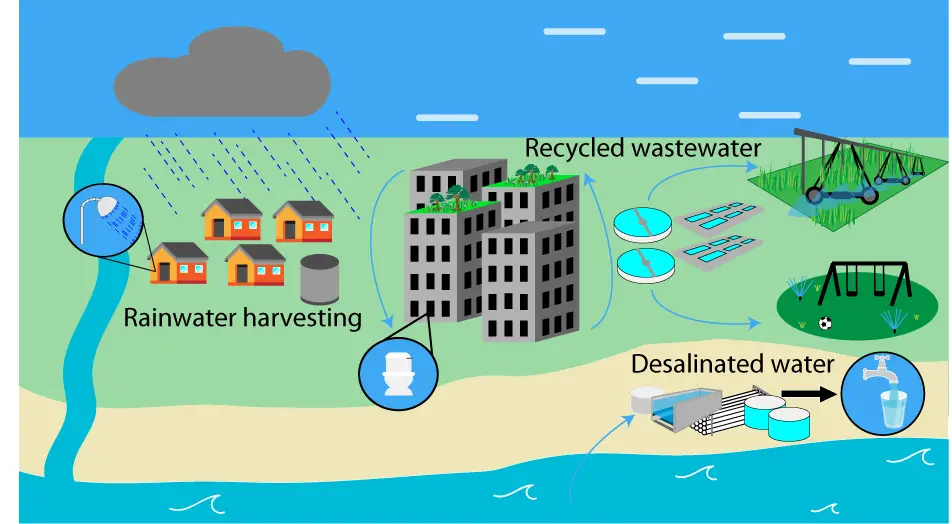
Sustainable infrastructure development also considers the environmental impact of water distribution planning. This includes minimizing energy consumption, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and protecting natural resources. Implementing green infrastructure practices, such as rainwater harvesting, water recycling and sustainable drainage systems, can help mitigate the environmental impact and promote a more sustainable water distribution system.
Financial Considerations
Financing plays a significant role in municipal water distribution planning. It is essential to assess the financial resources available and identify potential funding options for infrastructure development and maintenance. This may include government grants, public-private partnerships, or user fees. A comprehensive financial plan ensures the long-term sustainability of the water distribution system.
Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders, including the community, local authorities and water utility providers, is crucial for successful municipal water distribution planning. Collaboration and communication with all relevant parties help identify their needs, address concerns and ensure the development of a sustainable and inclusive water distribution system that meets the requirements of the community.
Planning for the Future
Planning for the future is crucial in municipal water distribution. As communities grow and evolve, it is essential to anticipate future water demands and plan accordingly. Sustainable infrastructure development plays a vital role in ensuring long-term water supply and resilience.
One aspect of planning for the future is implementing water reuse and recycling systems. By treating and reusing wastewater, municipalities can reduce their reliance on freshwater sources and ensure a sustainable water supply. Additionally, exploring alternative water sources, such as rainwater harvesting and desalination, can help diversify water supplies and enhance resilience.
Furthermore, integrating smart technologies and data analytics into water distribution systems can improve efficiency and enable proactive maintenance. Real-time monitoring and analysis of water usage and infrastructure performance can help identify potential issues and optimize operations.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, municipal water distribution planning is a critical aspect of sustainable infrastructure development. By considering key factors such as water availability, aging infrastructure and climate change, municipalities can ensure a reliable and efficient water supply to their communities.
Overcoming challenges through demand management, infrastructure upgrades and water quality management is essential for effective water distribution planning. The economic and environmental benefits of such planning are significant, promoting economic growth, cost savings and environmental sustainability. Planning for the future and implementing sustainable infrastructure development strategies are crucial to meet the evolving water demands of growing communities.
















