When you’re thinking about the best type of foundation for a soil type that lacks firm strata or bedrock; you’re left with two options – pier foundation or pile foundation. Pier foundation is ideal for smaller applications. They can easily act as a stable foundation for sheds or small living units. On the other hand, pile foundation is best for supporting greater loads of highways and bridges.
Homeowner’s prefer slab at grade foundation due to affordability and overall stability. However, slab-at-grade is not always a feasible choice. Slab-on-grade not only sets the house rest very low to the ground but also make it susceptible to flooding. Pier foundation on the other hand brings in plethora of benefits.
Can you relate this scenario with the foundation of a beach house? They’re usually built on stilts. Most of the houses are built to have a pier or pier and beam foundation. You can visualize a pier foundation by looking at a wood deck. Pier foundation serves best for sites where it is difficult to dig a traditional foundation. They’re also ideal for areas close to oceans and for scenarios where you need to raise your house up in order to protect from floods and rising tides.
So, let’s see some of the insights about pier foundation:
What is a Pier Foundation?
A pier foundation is also sometimes referred to as a “post foundation. In a typical arrangement, it consists of large diameter cylindrical columns that support the superstructure. It helps in transferring substantial super-imposed pressures to the hard strata underneath. It rises to numerous floors above earth.
A pier foundation is a bit different than a pile foundation, aside from the obvious depth difference. Former type of foundation has a vertical column with a bigger cross-section than a pile. A pile foundation is built in a dry environment by drilling a large diameter cylindrical hole to the proper depth and then backfilled with concrete.
Also Read: What is a Pier and Beam Foundation? Cost, Pros Cons
Difference between pile and pier foundation
A pile foundation works well when the top layer is made up of decomposed or poor rock and the bottom layer is made up of sound rocks. In some cases, moving the bearing pile through decomposed rock may be challenging.
In the case of hard clays, which are resistant to supporting pile driving, the pier foundation may be quite simple to construct. To transfer loads, piling foundations utilize both friction and bearing, whereas pier foundations just use bearing.
Cost of pier foundation
So, while you’re comparing different choices for making a solid foundation for your house, cost is definitely a key factor. A lot of builders believe that pier foundation is costlier than slab at grade. However, your cost for foundation depends on the region you’re in, your site, and the loading you want to transfer. However, a significant saving in pier foundation is during repairs. A slab foundation is too costly and difficult to repair. On the other hand, a pier foundation can be easily fixed. You can even fix one or two pier if the settlement or problem is localized.
Also Read: Deep Foundation – Types – Uses – Advantages – PDF
Types of Pier Foundation
Masonry Foundation
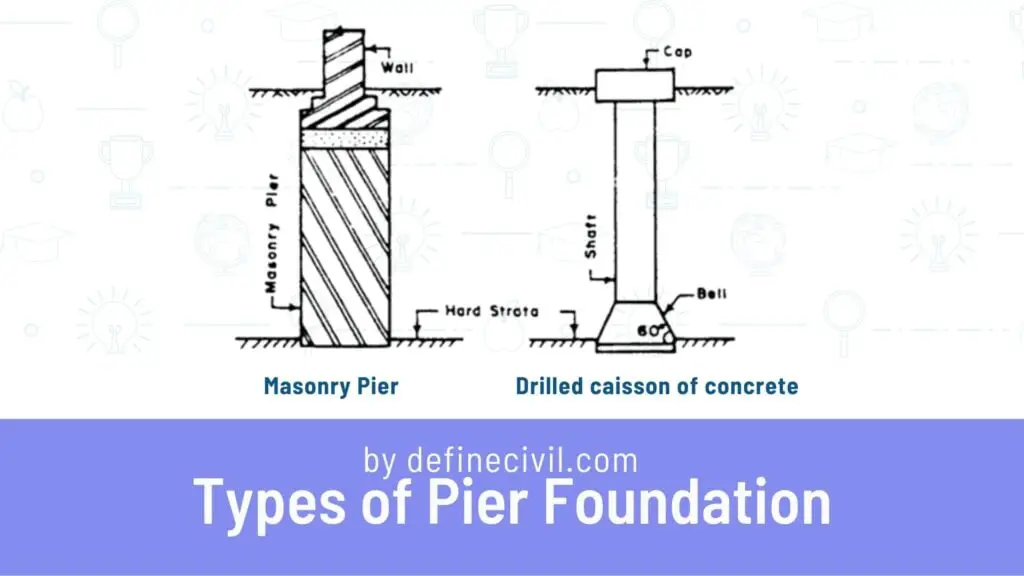
Masonry piers are used when there are solid soil layers at shallow depths. It is possible to extend the masonry pier up to a depth of 4-5 meters. As the depth of the hard soil layer increases, building a foundation of this type becomes more challenging. Masonry pier foundations come in a wide range of shapes and sizes, including circular, rectangular, hexagonal, and other shapes. Many antique structures were erected on pier foundations, despite the fact that concrete had not yet been invented. Pier foundations were also often utilized before to 1950.
Concrete Pier
In that they serve the same purpose as masonry pier foundations, concrete pier foundations are similar to masonry pier foundations. A concrete pier’s size or diameter is comparable to that of a masonry pier due to its high load-bearing capacity. Because different shapes are difficult to create, most concrete piers are round, square, or rectangular.
Pier foundations are available in a wide range of forms and sizes.
- The construction was supported directly on the pier foundation by the solid soil layer. Piers are spaced at regular intervals in these types of foundation systems.
- A network of piers supports the structure. Piers, on the other hand, are erected on hard soil or rock to support superstructures and are connected by a foundation slab.
Drilled Pier
Concrete foundations in the shape of a cylindrical cylinder are known as drilled caissons. The goal is to use concrete or caisson foundations to support the superstructures’ rising axial loads.
Drilled caisson foundations, unlike masonry/concrete pier foundations, may be built to a higher depth. Furthermore, for these types of foundations, mechanical excavation may be employed.
There are three types of foundations on the market.
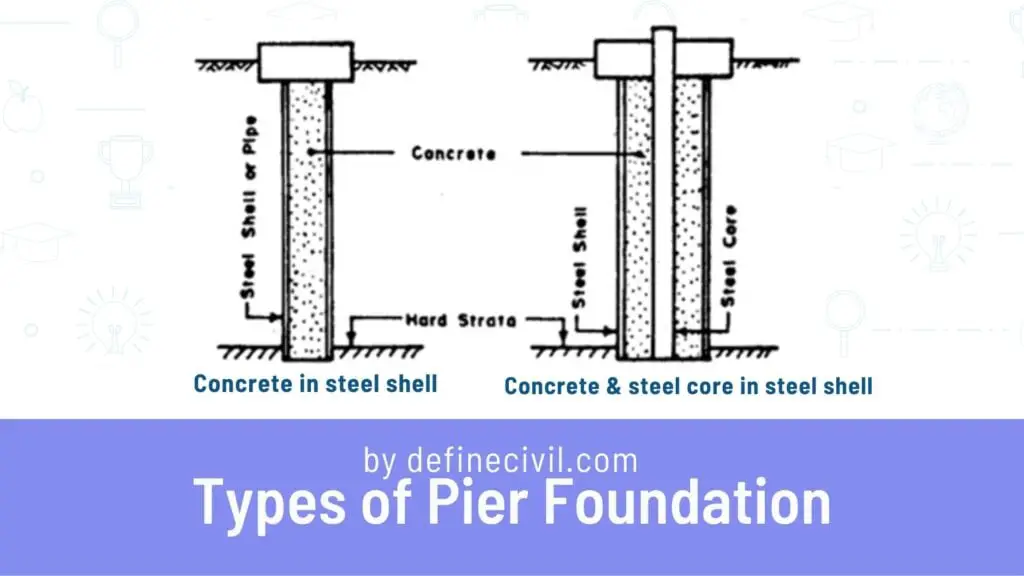
- Caissons made of concrete with drilled holes and a longer bottom.
- Concrete caissons are made by pouring concrete into steel pipes.
- Concrete caissons with a concrete and steel core in steel pipes.
The accompanying diagram shows the three main types of concrete caisson foundations, in addition to the masonry pier foundation.
Advantages
- On the land, piers of any length and size are permitted.
- Work may be completed quickly since construction equipment is often transportable.
- Inspection of drilled holes is possible due to the increased diameter of the shafts.
- A single drilled pier foundation may resist tremendous weights without the use of a pile cap.
- The drilled pier may be employed in a variety of soil conditions.
- As the project continues, changes to the design requirements may be made. Drilled piers do not have as much ground vibration as driven piles.
- Underreaming the bearing’s bottom may increase its capacity (in non-caving materials)
Disadvantages
- All materials used in the building of drilled piers must be rigorously inspected for quality.
- It is inconvenient to go through the operation. It will need sufficient storage room to handle all of the construction materials.
- With drilled pier construction, the benefit of increased bearing capacity due to granular soil compaction that may be obtained with driven piles is not accessible.
- In regions where there is a considerable flow of ground water due to artesian pressure, drilled piers are particularly difficult to construct.
Preferred Pier construction conditions
In the following instances, a pier foundation is used:
- Pier foundations are employed when there are decomposed rocks in the top layers and sound rock strata underneath them.
- Pier foundations can be employed in this situation since stiff clays provide a lot of resistance while driving a bearing pile.
- Because the pillars are modest in comparison to other foundations, it is utilized if the home is made of logs, timber, or frame.
- Pier foundations are utilized when a structure must be erected on a slope.
- Otherwise, the pillars will sink under the weight of the structure if the soil has a limited water retention capacity.




















