No matter the type of road, drainage is an integral part of the design process. Be it a highway or a link road, the surface runoff is always there. Sometimes the highway engineer provides slope in the profile of the road to drain the surface water. But in some cases, the slope is not sufficient and it needs cross-slope with a ditch at the end to collect and dispose the runoff.
But road drainage is a vast subject of highway engineering. You need to be familiar with different types and the purpose they serve to pick the right type of drainage for your road.
Road Drainage
Drainage is the method of collection and removing of surface or sub-surface water. It is done to prevent accumulation of water which can cause different problems to structures or buildings. In case of agriculture, sub-surface water causes water logging, while in case of building foundation sub-surface water causes wetting and drying of soil that results in differential settlement of building, cracks in building, and other severe problems.
Purpose & Function
Similarly, road drainage includes interception and removal of water from, over and under road surface. This is done to maintain stability and durability of road surface because road surface is highly sensitive to water whether it is surface or sub-surface water. Surface water present on road causes freeze and thaw which results in cracks, rutting of road surface. Whenever water gets contact with subgrade it causes decrease in soil thus results in functional failure of road surface. Therefore, it is dire need to provide proper road drainage for durable road surface.
Types of Road Drainage:
Primarily, road drainage is divided into two main types that includes:
- Surface Drainage
- Sub- Surface Drainage

- Surface Drainage:
It is the collection and removal of water from road surface for efficiently and safely moving of traffic on road. This surface drainage is provided in initial stages of highway construction which prevents the flowing of surface water from pavement into shoulder or in any other layer. Other functions, included for surface drainage are:
- To keep road surface dry
- It allows efficient movement of traffic
- It increase durability and stability of road surface
- It collect water from road surface and dispose to nearby stream
Surface drainage consists of following two operations
- Collection of surface water
- Disposal of collected surface water
Also Read: Sheepsfoot Roller- Design- Applications- Mechanism
- Collection of Surface Water:
Longitudinal side drains or ditches are usually provided for the purpose of collecting surface water. These side drains may be of V-shaped or trapezoidal shape. Trapezoidal shaped side drains are considered that they are efficient and has high capacity.
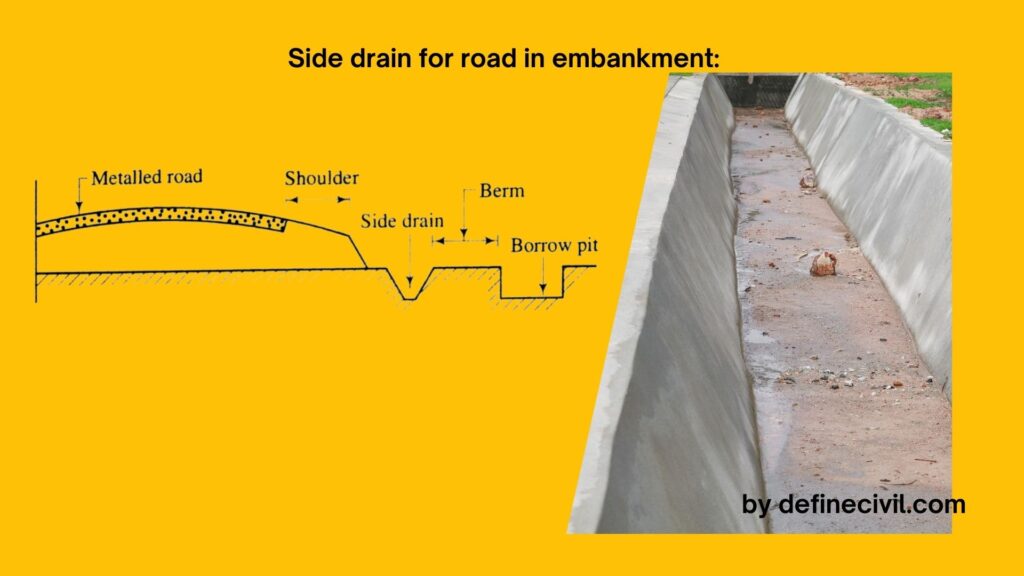
- Side drain for road in embankment:
In case of embankment, side drains are provided on both side of road beyond the shoulder. These drains are provided at distance of about 2m from embankment, so that drain water does not enter in earth work.
These side drain collects rainwater falling on adjacent land and dispose into nearby stream without damaging embankment or road structure.
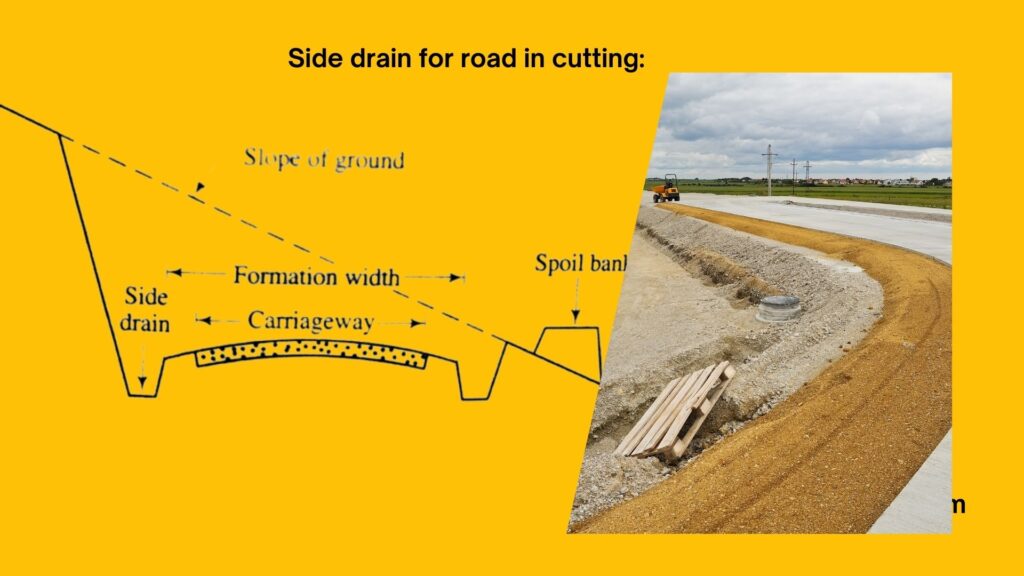
- Side drains for road in cutting:
In case of road provided in cutting areas, side drains are provided on either side of carriageway. These are designed in such a way, that they don’t overflow and damage road surface
- Ditches: It is small to moderate depression created for flowing of water. It is provided alongside roadways or fields whose main purpose is to collect rainwater and provide efficient drainage.
- Disposal of collected water:
To provide effective drainage, second operation of surface drainage is disposal of collected water in nearby stream or lake. Cross drainage work like culverts or bridges are provided for disposal of surface water from side drains.
Cross drainage Structures: Whenever, stream has to pass roadway or side drains are to dispose in stream or valley, drainage system is provided that is called cross drainage system which includes culverts and bridges.
Culverts: Tunnel like structure which allows water to pass through a road is called culvert. This is permanent drainage structure having span length less than 6m.
These culverts are divided into four types which includes:
- Arch Culvert
- Open or Slab Culvert
- Box Culvert
- Pipe Culvert
Also Read: Curbs and Gutter – Details
Design of Road drainage system
In case of design for surface drainage, it is considered that the slope provided in longitudinal side drains is enough to drain water efficiently so as to provide effective drainage system. However, side drains are designed on the basis of following two considerations
Hydrologic Analysis: It includes the study of water movement on earth surface, quantity of water flow, runoff from precipitation, magnitude of flood and frequency of occurring. Following equation is used:
Q= CIAd
Where Q= runoff, C= runoff coefficient, I= intensity of rainfall, Ad= drainage area in 1000-meter squares.
Hydraulic Analysis: It includes the study of flows of liquid which depicts how to provide efficient drainage system that is secured for property or highway structures. The equation used is:
Q= A.V
Area of side drain will be calculated using above equation. While velocity of flow and longitudinal slope inside drain will be calculated using Manning Formula: V=1/n( R^(2/3) * s^(1/2))
- Sub-Surface Drainage:
It is found that any moisture content or water present in sub grade or below the pavement causes decrease in strength of soil, and disintegration of road structure in case of heavy traffic. So, the drainage system constructed for diversion or removal of excess water from sub-grade is called sub surface drainage system.
Main purpose of sub-surface drainage include:
- Lowering of water table.
- Seepage Control
- To control capillary rise.
Lowering of Water Table
If water table is higher than 1.5m below the sub-grade, then there is no need of providing sub-surface drainage. While if this difference is less than sub-surface drainage system is provided to bring down the water table. This is done by providing longitudinal sub-drains or pipe drains below the ground surface in a permeable soil stratum. These longitudinal drains are provided on both sides of road or in the center as well. If transverse drainpipes are not suitable to lower water table, then transverse drains are also provided.
Seepage Control
If ground surface is sloping towards pavement, then there are chances that seepage will take place. If vertical distance between subgrade and seepage level is between 60 to 90cm then subsurface drainage is provided to prevent entry of seepage into subgrade,
To Control Capillary Rise
It is the rising of ground water towards subgrade, which causes decrease in strength of soil and structural disintegration of road. So, there is need to control capillary rise which is done by providing granular layer of suitable thickness and by providing bituminous or impermeable layer instead of granular layer
Advantages
- It makes durable road surface.
- It helps in movement of traffic smoothly.
- It helps in effective removal of rainwater from road or surrounding ground.
- It prevents accumulation of water.
Disadvantages
- Higher initial cost is required for installing drainage system.
- Experienced and skillful workers are required
- Maintenance work is needed.
- Repair work is costly and inconvenient.
















![Engineering Communication by Knisely [PDF] [FREE DOWNLOAD]](https://definecivil.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Editorial-Markup-Stop-Start-Continue-Brainstorm-Presentation-100x100.jpg)