The uses of Bentonite Slurry in Pile Foundation and diaphragm walling wherein the bentonite is defined as excavation supporting slurry, lining tube or drilling mud are very similar and are considered one and the same.
Due to the application of Bentonite slurry in construction it is sometimes referred as retainer, sealant and stay-insular.
The essential condition for the successful piling operation in case of bored cast in-situ piles is a fine-grained soil which will stand without support until a temporary steel tubular liner is lowered down the completed hole.
But in case of granular soil, or in order to make excavation more economical by avoiding the excessive use of steel liners bentonite slurry is to be used as stabilizing suspension or drilling mud.

Why use bentonite slurry in pile foundation?
Whether you use power-driven rotary auger drills, casing oscillators, continuous flight auger drilling rigs or reverse circulation drilling rig in all of such cases either you have to use lining tubes or casings to support the sides of the boreholes of you have to opt bentonite.
Even in stiff fine-grained soils, the side of the bore hole is subjected to many types of forces and pressures including active earth pressure, overburden pressure, hydrostatic or pore water pressure.
Beside this, fissures may also be there that contain pockets of sand that can collapse into the bore holes, resulting discontinuities in the pile shaft.
What actually is the bentonite slurry?
Bentonite is the name used for a range of clays that can swell and gel when mixed with water.
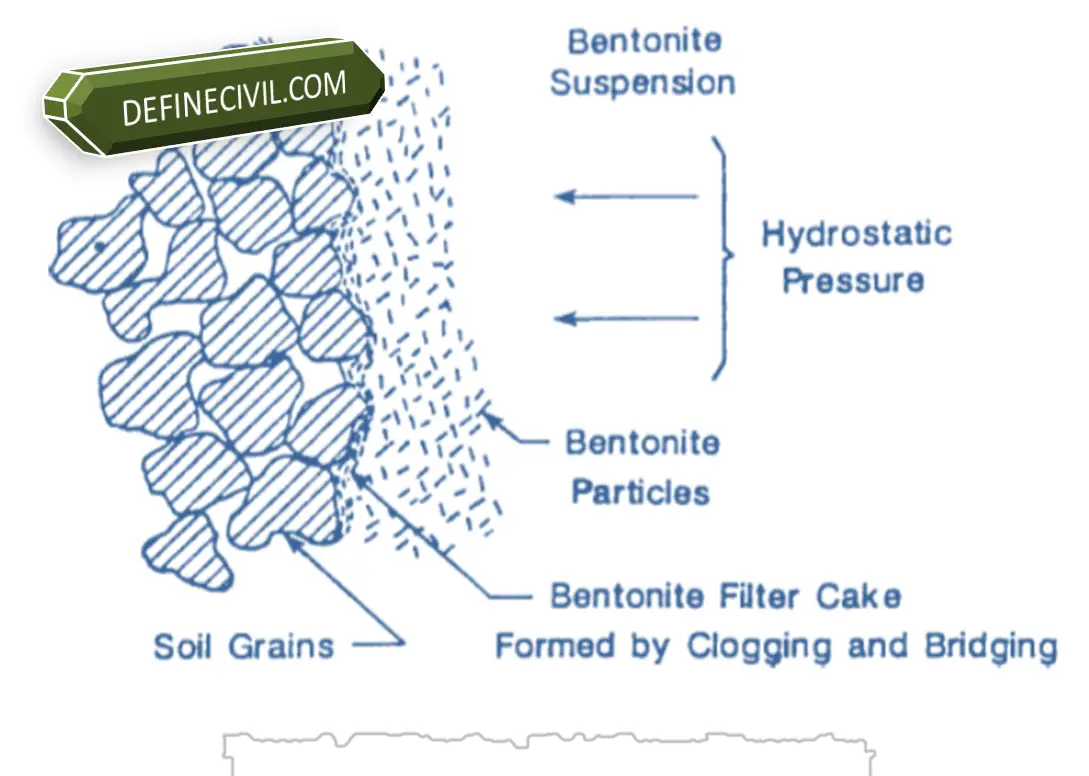
Bentonite is naturally found in form of sodium montmorillonite which exhibits thixotropic properties i.e. when bentonite is mixed with water it form a gel under static conditions but when disturbed or when distressed it regains its fluidity.
During piling operation i.e. auger boring, the slurry is continually agitated thus penetrating into walls of the borehole converting it into an impervious filter cake that has adequate power to counteract the hydrostatic pressure of slurry.
The stability of boreholes is dependent on the hydrostatic pressure produced by bentonite.
This hydrostatic pressure must be larger than sum of net soil pressure as well as pore water pressure.
According to the electric nature of Bentonite suspension, in static conditions of bore hole it has exchangeable sodium cations (positively charged ions) that create a weak electrical bond thus converting into a jelly as mechanical structure.
But when dispersed, as in free flow conditions, the electrical bond breaks into particles having negative charge on surface and positive charge in the edges.
The history of slurry usage in drilling works date back to 1960’s where they were practically used in drilling works for oil wells. Beforehand the drilling holes were supported by casing and thus encompassing a major share of budget in drilling works.
From there onwards practical and technical knowledge were established about application in foundation drilling. With the enhancement in understanding of slurry material properties as well as numerous failure of drilling projects, lot of adjustments were made to their physical properties and recycling process.
Properties Bentonite Must Have
The bentonite to be used in pile foundation must have following characteristics :-
- It must support the excavated bore hole for pile by exerting hydrostatic pressure on the sides.
- It must remain within the pile bore hole and must not flow into the soil to great extent.
- It must suspend the debris or waste and must prevent formation of sludgy layers at the base of the hole.
- It must have no significant interference with the bond between reinforcement of pile and concrete.
- It must render clean displacement when converted to fluid by concrete.
- It must be able to remove suspended debris and could be re-used easily by passing through screens and hydrocyclones.
- Bentonite slurry must be easy to pump.
In a clay soil there is no penetration of the slurry but the hydrostatic pressure of the fluid, which has a density of around 1040 kg/m3, prevents collapse where the soil is weakened by fissures.
Specification of Bentonite Slurry
As per IS; 2911 – Part 1 / sec 2
The bentonite suspension used for pilling work shall satisfy the following requirements.
- Density of freshly prepared bentonite : Between 1.0325 to 1.1 g / ml
- Liquid limit : More than 300 % & less than 450%
- Marsh viscosity : 30 to 60 seconds
- Swelling index : At least 200% of dry volume
- PH Value : Between 9 & 11.5
- Sand content: Less than 7%
- Silt content: Less than 1%
Arrangement for use of Bentonite slurry in Pile Foundation
- Bentonite Pit
Near the location of the pile bore a temporary bentonite pit of suitable size is excavated and a vertical pump is fitted in it.
- Bentonite Feed Tank
A bentonite feed tank is provided near the pit for the storage of fresh and recovered slurry of bentonite.
- Temporary Channel
Around the pile bore, number of sacks / sand bags filled with soil is connected to make a temporary wall and channel in the form of small cofferdam.
This barrier will guide and direct the mixture of bentonite and mud coming out from the bore during piling operation towards the bentonite pit.
The vertical pump in the bentonite pit would pump the slurry of mud and bentonite to the recovery tank for necessary desilting when required.
- Recovery Tank
- This tank is connected to both bentonite pit and bentonite feed storage tank. The bentonite when required to be desilted for reuse is pumped to the recovery tank from the bentonite pit and then after getting recovered is transferred to the bentonite storage tank.
- The slurry-soil mixture that is discharged from the bore hole is allowed to settle in lagoons / tanks to remove soil particles.
- It is further cleaned in a cyclone, and chemicals to aid gelling are added before the reconditioned slurry is pumped into a holding tank and then returned to the pile bore hole.
- Location of Tanks
The location of the both bentonite storage and recovery tanks is selected keeping in view it’s repetitive and efficient use. It is recommended that the position of tanks must be such that it can cater minimum four pile foundation locations on either side.
- Supply of Bentonite during drilling
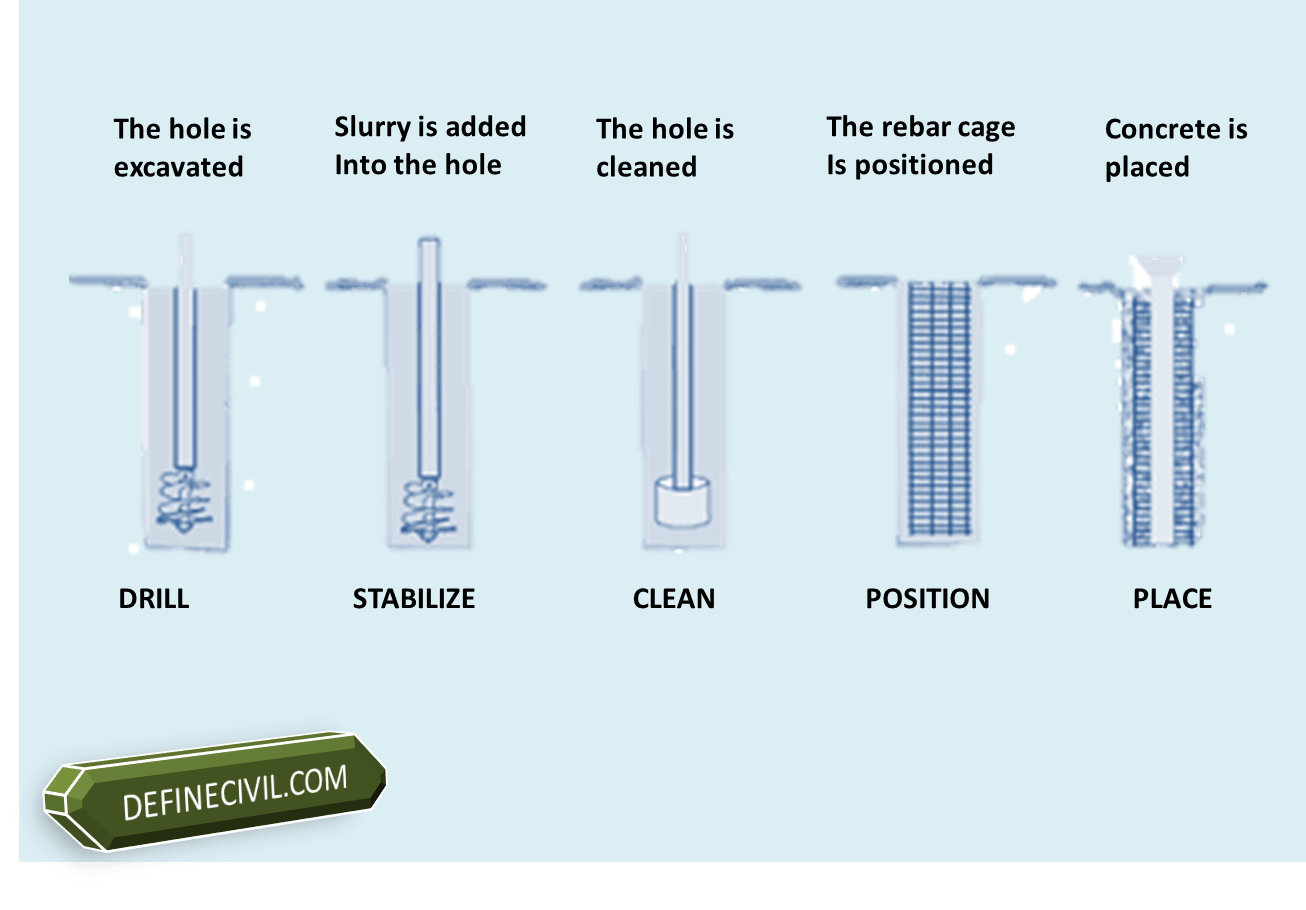
Bentonite slurry is used in a simple / crude way along with rotary auger equipment when drilling pile boreholes through sands and gravels to obtain deeper penetration into stiff fine-grained soils.
The hole must be augered through the sands and gravels without support, and then the casing is lowered down.
The hose of pump installed on the bentonite storage tank, is connected to the top of drilling pipe transferring fresh bentonite slurry to the borehole. After the borehole is filled up to the top the bentonite flows back to the pit along with mud.
In this way the mud from the borehole produced during drilling operation is directed to the bentonite pit.
- Flushing
In this way the drill pipes that were attached to the chisel are connected one by one till the required depth of the borehole is achieved.
During drilling operation, the flushing / treating of the bentonite is done simultaneously to maintain the specific gravity of suspension between 1.05 to 1.12.
After removal of the auger / chisel, the borehole is flushed completely to remove all the impurities.
- Reinforcement and Concrete
After that reinforcement cage is lowered immediately keeping in view the centerline as well as verticality of the pile borehole.
Concreting is finally done by tremie method thereby replacing the bentonite solution up to 1 meter above the pile cut off level.
Before installation of casing, the support may be provided while drilling by means of a bentonite slurry.
Where the depth of coarse-grained soil is relatively small it is uneconomical to bring in high speed mixers, slurry tanks, pumps and reconditioning plan for normal employment of bentonite techniques.
Instead, a few bags of the dry bentonite are dumped into the pile borehole and mixed with the groundwater or by adding water to form a crude slurry which is adequate to smear the wall of the borehole and give it the necessary short-term support.
After drilling through the granular overburden, the casing is lowered in one or more lengths and pushed down to seal it into the stiff fine-grained soil below.
Use of Bentonite to Aid Drilling while Pilling
The use of bentoite slurrut y to aid drilling with or without temporary lining tubes may cause some difficulties when placing concrete in the pile. For example, if the slurry becomes overloaded with solids from excavation, a thick filter cake will be formed and may not be removed by scouring during concreting.
In such cases it may be necessary to use a mechanical scraper to remove the excess filter cake prior to concreting.
But wait that’s not all….
FINAL WORDS
Bentonite is not just used in pile operation; it has numerous other applications in the field of Civil Engineering. But recently a new concept of polymer support fluids have emerged.
These fluids are although more expansive than bentonite at initial cost but they can be disposed of easily by neutralizing in to the existing drains. But in case of Bentonite frequent de-sanding is required and is treated as ‘hazardous’ under pollution and control regulations.
So in coming days I would try to discuss about other applications of bentonite as well as the use of polymer fluids. So stay tuned to definecivil – home of civil engineers.
And don’t forget to share our articles with your friends.