Stem walls on concrete foundations are popular in the construction industry of America and Canada and make up the spinal cord of one of the five common and basic types of construction footings in the USA. Here is the entire mechanism behind how such small walls manage to hold up such large structures
What is a Stem Wall?
A type of footing that is typical across the USA, a stem wall is essentially a short supporting wall that forms a connection between the foundation of a structure and the vertical, load-bearing walls of the superstructure that sits atop of the ground. These walls help in transferring the load of the superstructure to the footing, which then distributes the loads over the area of the foundation.

Stem wall meaning
Stem walls are usually constructed with houses that have crawl spaces and are widely popular in areas such as California, Northwestern areas, Texas, and areas to the south of USA. They are also a common preference of the designers and engineers when designing structures in an earthquake prone area.
Houses with full basements, such as the ones popular in mid-Atlantic, Northeast and the Midwest, or structures build in coastal areas or such structures that are build on piers and piles to raise them above flood levels should avoid the usage of stem walls.
Stem wall detail
These walls are usually made from either concrete or masonry blocks. Even though concrete stem walls have a greater strength, which is required in some cases, but they require the installation of bracings, hence increasing the cost and can also require extra visits from the site engineer. In some structures, using preservative treated wood in the construction of stem walls is considered a low-cost solution.

Cost
The cost of the stem wall depends on the length or the scope or work, depth of the wall, height of the wall, and the availability of material. Typically, the cost varies between $7,000 to $21,000.
Construction of Stem walls.
There are many ways to construct a stem wall, but all have some initial steps common, and we will now talk about those steps:
Step 1 Get the construction site cleared
The construction site must be cleared before the construction of the wall. Any debris, large stumps or plant material must be removed, and it must be checked with the local government if any of the trees in the vicinity are protected.
Step 2 Get the underlying soil compacted
The soil must be well compacted and additions, like gravel must be to achieve the required strength. For smaller projects a plate compactor would be sufficient but for larger projects equipment like rollers would be needed.
Step 3 Pour the concrete for the foundation
The concrete foundations for the stem wall must be a minimum of 12” or 1’ below the undisturbed strata and the frost line with a minimum with of 12” or 1’ but the exact size of the foundation will vary based on the load of the superstructure, the type of strata underneath, its bearing capacity and compaction.
Vertical bars should be used during the construction to ensure that the wall doesn’t slide off the foundation, especially in areas that are prone to earthquakes. After the stem wall has been constructed, a sill plate is attached to it with anchor bolts.
Stem wall Foundation Benefits
There are countless reasons why these walls are popular, and we will discuss the major ones here:
- Solid
The walls transmit load of the superstructure to the foundation and the foundation then distributes it on its area
- Protection to the structure
Since the base of the structure is lifted, the structure is provided protection against natural hazards such as flooding.
- Access is easily provided
Plumbing, wiring and different mechanical and electrical issues can be easily sorted due to easy access provided by stem walls.
- Adds to the aesthetics of the structure
The structure gets elevated and looks grander and more appealing.
Disadvantages of a stem wall
The disadvantages of a stem wall are:
- They are more labor intensive requiring high number of labors
- Backfilling is required
- They are more time consuming
Stem wall vs Slab
Here’s how stem wall differs from a monolithic slab
In some of the warmer parts of the states, monolithic slabs are popularly used as an alternative to stem walls, which is essentially a single thick slab poured under the entire area covered by the load bearing walls.
The main advantage that monolithic slabs have over the stem walls is that they are less expensive and less time consuming to build and since the structures don’t have a crawl space, the client doesn’t have to worry about maintaining it.
The slabs are common in tropical areas, areas where the ground doesn’t freeze and, in the USA, they are usually limited to outer structures like sheds or garages.
But even in warm climates when the soil isn’t compacted properly, these slabs may not pe appropriate to install. They also may generate crack along the sections under the structural walls.
Concrete Stem wall design
So, you might be wondering how thick should be the concrete stem wall?
- Design Intent: We design concrete stem wall as retaining walls. It has a strip or a pad at the bottom with loading applied on the top on the fill material.
- Design Code: Most of the designs follow IRC 2003 Code.
- Height: As per the 2003 IRC Code the maximum height of the stem wall is 4 feet. For more than 4 feet high wall additional reinforcement is required.
- Width/thickness of the wall: The minimum width of the stem wall is 6” for single story buildings while for 2-story you need to provide 8” minimum.
- Footing Pad: The bottom footing pad is 12” minimum while for 2 stories it is 15” minimum. Depth: While the thickness of the footing pad is between 6” and 7”. The minimum depth of the footing pad from the grade to bottom of footing is 24”.
- Pouring sequence: Mostly 2 pour system is used for pouring the slab. The footing pad is poured with projecting steel bars while the upper wall is build afterwards with cold joint or construction joint in between.
- Reinforcement: A “J” shaped vertical rebar is provided with #4 diameters with over the center spacing of 48” having 90” hook at the end to make it monolithic with the footing pad. 2 horizontal rebars are provided one at the footing hook while one from 12” at the top.
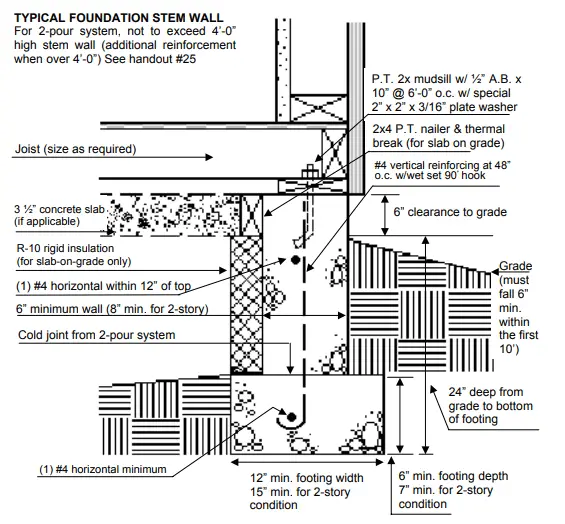
As per ACI-318-Section 22.10, for the foundation systems consisting of a plain concrete footing and a plain concrete stem wall, a minimum of one bar shall be provided at the top of the stem wall and at the bottom of the footing.
Chain Wall foundation
Another name for stem wall foundation is chain wall foundation. Chain wall is in the form a raised wall foundation that can be of concrete or cmu blocks. It helps raise the foundation above the flood level. Sometimes you can use chain wall to extend the standard foundation of a house. The main difference between a stem wall and a chain wall is that chain wall foundation is filled with backfill. Stem wall on the other hand don’t necessarily have to be filled. The inside space in that case can’t be used as a crawl space.
We call it chain wall – as the wall acts as a chain or a cage of concrete pillars that retains the fill material. The fill has to be compacted structural fill. For further stabilizing the fill, we can add cement to the soil.
Precast chain wall foundation
Precast chain walls are available in the market as intact units. All you’ve got to do is prepare the space and create a level ground. Afterwards, lower the chain wall by crane. In most precast chain wall, we don’t have to fill the inside.
So, if you’re looking to build a house in floor prone areas, you can opt for chain walls to raise the base slab as high as 20 meters above the road level.
Stem wall vs crawl space
A crawlspace and a stem wall are two same things or components in a home. A lot of people often wonder if they are two different things. Both include supporting the home above at some height of about 2 feet.
Stem wall vs retaining wall
They are also two same things. When someone says stem wall and they are referring to residential construction, they are referring to a retaining-type wall that usually comes off the corner of the foundation. Anyhow, tt’s a way to step down the grade around the house- especially if your house has a basement.
Monolithic Slab Vs Stem Wall
Apart from Stem walls, another predominant type of foundation for a new home is monolithic slab.
What is a mono slab foundation?
A monolithic slab or mono slab foundation is one single concrete slab foundation that is thick enough to carry the load from the load-bearing walls.
Monolithic slabs are much faster to build and are cheaper than stem walls. The labor cost is pretty low and it’s much easier to build.
Anyhow, mono slab foundation have got to be flat and straight. For that you might have to fill in some dirt and densely compact that to avoid settlement. So, if you build the monoslabs right and you use them under right conditions; it is going to stay for long – even longer than stem walls.
So, if you don’t need a crawlspace and there’s no danger as that of a flooding, better opt mono slabs. You got flat and single floor elevations. That’s the best part of having mono slabs in your home. But you need to evaluate your lot to know if the slope is not too much.
Anyhow, just like the pros; monolithic slab do have some pitfalls. If the ground in your lot is not level enough and you need to fill in a lot of dirt, it’s better to not go with monolithic slab. That’s because without proper compaction, the concrete mono slab is going to crack sooner or later.
Similarly, if you’re in need to build up your home above a flood plain as is the case with most homes in Florida; you can’t go with monolithic slab.
Anyhow, you can ask a structural engineer to evaluate your situation. A mono slab foundation build on too much filling can later have cracks around the perimeter walls and load bearing walls. Such cracking can further induce structural issues that are too difficult to correct.


















