Selecting the type of footing is an important aspect during new and renovation construction. With array of types it is best to know your options.
Building mainly consists of two components that include foundation or sub-structure and super structure. Foundation or sub-structure is the lowest part of structure which transmits load to a soil. While super structure is a part of structure which is above the ground level.
Soil which is located immediately below the base of foundation is called the sub-soil or foundation soil, while the lower most portion of the foundation which is in direct contact with the sub-soil is called footing.

Difference between Foundation and Footing:
- Foundation is the sub-structural part of building which is below ground level and its function is to distribute structural load evenly and provide stability to structure. While footing is the lower most portion of foundation which is in direct contact with soil and constructed with concrete or brick masonry. Main function of footing is to transfer vertical load directly to soil.
- All footings are foundation, but all foundations cannot footings. Foundation is lowest part of structure and transfer load from super structure to soil. There are two types of foundation that include shallow foundation and deep foundation. While footing is the part of foundation which transfer load to soil. Footing consists of slab or rebars. Unlike shallow or deep foundation types of footing include isolated footing, combined footing, continuous footing, strip footing, pile footing etc.
- Example of foundation or footing can be illustrated as, consider human body, actual feet of human body legs are called as footing while legs are considered as foundation.
Also Read: Continuous Footing – Detail – Diagram – 3 types (DETAILED GUIDE)
Functions of Foundation or Footing:
Main functions of foundation include:
- To transmit dead load, super imposed load, live load and wind load from building to soil on which building rests.
- To provide stability against sliding and overturning effects.
- To transmit load in such a way that settlements are within prescribed limit, and without causing cracks in building.
- To provide safety against distress due to soil movement.
Types of Foundation
Foundations are mainly classified into two types:
- Shallow Foundation
- Deep Foundation
If depth of foundation is equal or less than its width, then foundation is called as shallow foundation. While if depth is more than width of foundation then it called as deep foundation.
-
Shallow Foundation:
If depth of foundation is less than width of foundation than it will be treated as shallow foundation. Term footing is conjunction which is used with the type of shallow foundation. In shallow foundation, there are mainly following types of footing.
- Isolated Footing
- Combined Footing
- Mat or Raft Footing
- Strip Footing
- Strap Footing
These types of footings are described here:
-
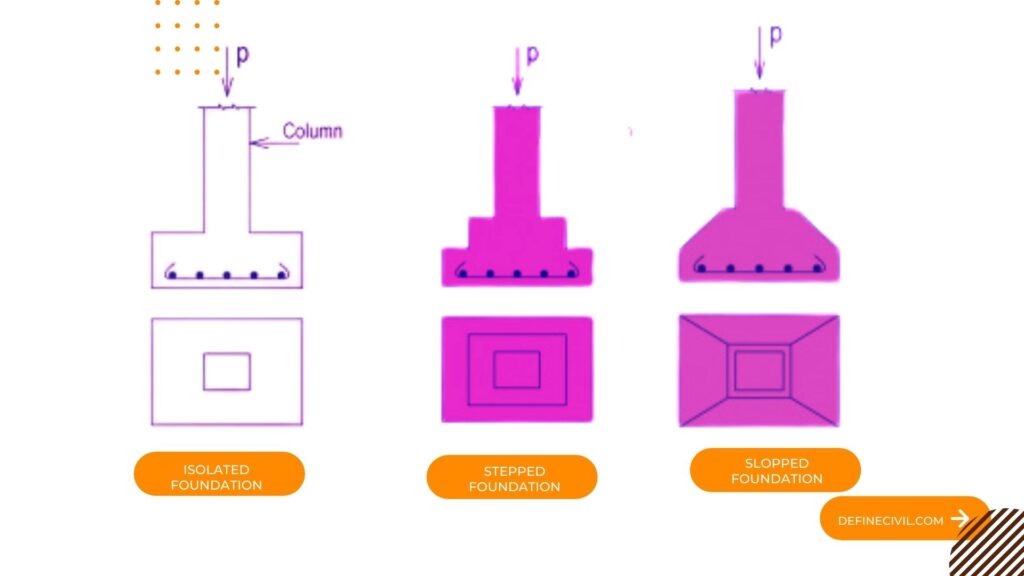
Isolated Footing:
It is a type of footing which is provided individually below columns. In this footing each column is provided with separately footings. This footing is laid on PCC and before PCC termite proofing spray is done to prevent footing from termite’s action.
This type of footing is provided when bearing capacity of soil is more than 24 kg/m^3.
Isolated footing may be of following types:
- Flat or Plain Footing: This type of isolated footing is generally square, rectangular, or circular in shape which is provided under each column independently. It is the simplest footing having square, rectangular or circular slab of uniform thickness.
- Stepped Footing: This type of footing is mostly used in residential buildings in which footings are stack upon each other just like steps which is shown below.
- Sloped Footing: Slope footings are trapezoidal in shape. They are made with great care that top angle maintained is of 45 degrees. As compared to stepped or plain footing it requires less concrete that’s why it is economical footing compared to other isolated footings. It is shown below:
-
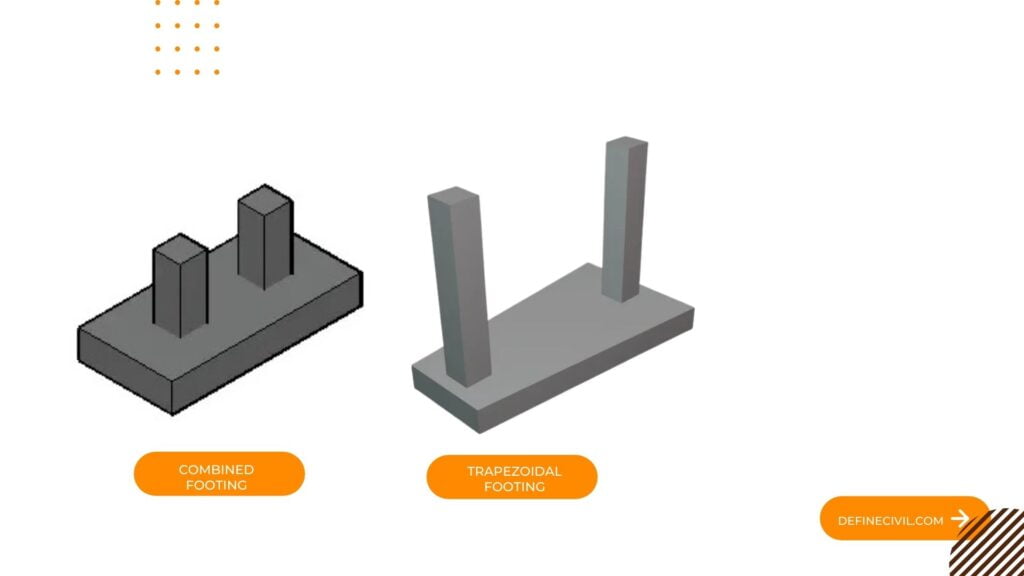
Combined Footing:
Common footing which is constructed for two or more column is known as combined footing. This type of footing is provided when available space is not enough to provide each column with separate footings, or two columns are so closed to each other that it is not possible to provide them separate footing.
Shape of combined footing includes rectangular and trapezoidal. Shape of combined footing is so proportioned that center of gravity of supporting area is in line with center of gravity of two column loads.
- Rectangular Combine footing: It is provided when loaded condition is such that either of two columns are equally loaded or interior column carries greater load.
- Trapezoidal Combine Footing: It can be provided for any type of loading condition.
-
Mat or Raft Foundation:
Foundation consisting of thick reinforced concrete slab covering the entire area of the bottom of structure is known as raft or mat foundation. It is provided:
- When building loads are high and safe bearing capacity of soil is low, and the required footing area becomes more than half the total area of structure.
- When there are strong soil strata below weak soil strata then mat or raft foundation provided.
- When bearing capacity of soil is less than 24kg/m^3 then mat foundation is provided.
- It is provided in coastal or seashore area where water table is very high.
- When elevator is provided in building than separate mat for elevator also provided.
-
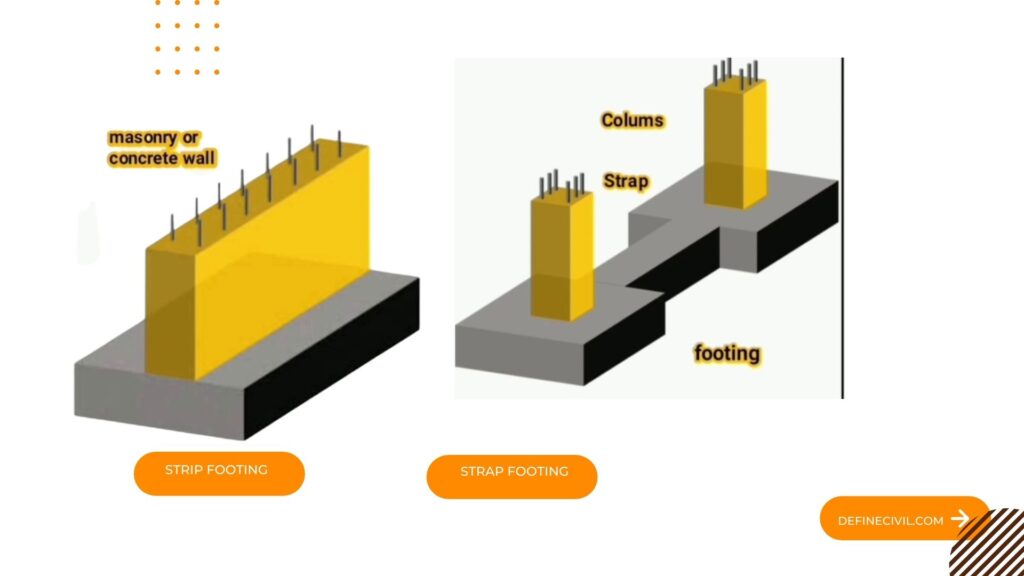
Strip Footing:
This type of footing is also known as wall footing. It is provided for load bearing walls. It consists of strip of concrete that spreads the weight of load bearing wall across an area of soil. Width of strip foundation depends upon type of bearing capacity of soil. Greater the bearing capacity lesser the width of strip.
-
Strap Footing:
It is a type of footing in which two or more footings are connected by beam. It is used where distance between columns is so great that combined trapezoidal footing become quite narrow with high bending moments.
-
Deep Foundation:
When depth of foundation is more than its width then type of foundation is called deep foundation. In this foundation depth to width ratio is more than 4 to 5. It includes following types of footing:
- Pile Footing
- Pier Footing
- Caisson or Well Footing
Pile Footing:
Pile is a long vertical load transferring member composed of either steel, timber or concrete. In pile foundation number of piles are delivered into base of structure. It is provided:
- When Soil is compressible, water-logged, and made-up type.
- When soil of suitable bearing capacity is available below the certain depth of structure. So, pile is provided to transfer building load to that strong bearing capacity of soil strata.
- When loading conditions are such that shallow foundation is not suitable to carry that load, then pile footing is provided for safely transfer of load.
Also Read: Pier and Beam foundation
Classification of piles:
- Precast Piles: Such types of piles are constructed in building and then transfer to site. These are ready made piles and used where land is not enough to cast piles on site. Length of precast piles varies from 4m to 30m and their load bearing capacity is designed for about 800kN.
- Cast in-situ Piles: Such types of piles are casted on site and do not require any transportation. These piles are casted below the ground surface and may be reinforced or not reinforced depending upon condition. These piles are designed for maximum load of 750kN.
Pier Footing:
It is a type of deep foundation in which hollow vertical shafts are sunk up to hard soil strata and then hollow portion is filled up with inert material like sand or lean concrete. Such type of footing is suitable for heavy structures such as flyovers in sandy soil or soft soil overlying hard bed at reasonable depth.
Also Read: Pier foundation
Caisson or Well Foundation:
It is a foundation which consists of a box of timber, metal, reinforced concrete or masonry which is open both at the top or bottom and used for building and bridge foundation. It is mostly used for bridges.
Also Read: Caisson Foundation – Types