A foundation failure is when it is no longer able to support the full weight of the building due to movement of soil and excessive settlement. In such cases, the building may sink or may topple over altogether due to inadequate bearing capacity.
Many foundation fail just because of improper assessment of soil conditions existing to the site. In some cases the buildings are constructed on marginal land due to lack of suitable land.
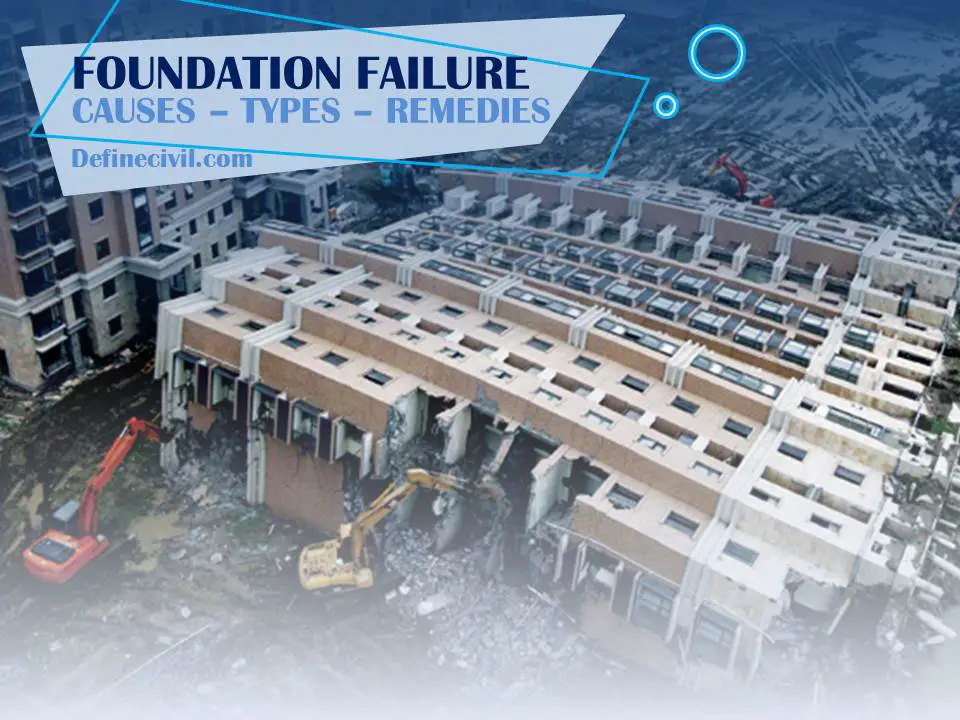
What is foundation failure?
Identification of foundation failure is very important to provide needful treatment. The failure modes of foundation are asymmetry and are complex to understand. Anyhow, in this read I’d like to shed some light on some common causes and types of foundation failure.
The foundation failure is rare these days because of accurate estimation of bearing capacity anyhow it can be catastrophic. The pile foundation can even fail because of improper site execution even though you’ve set all parameters correct.
What are causes of foundation failures?
According to Roddies, there is a difference between a deflection and failure of foundation. A limited deflection and settlement in a foundation that cause certain amount of cracking could be a deflection. A failure, on the other hand is caused by an excessive settlement and deflection that can cause serious damage to ceiling, floor finishing and partitions of a home.
If you’re a home owner and are worried about the cracks in walls and floors you might have to hire a Geotech expert to look for foundation condition. Because the foundation provides a base for the super-structure which transmits the entire load of the building to underneath soil on a broader area; the foundation failure is critical.
The foundation acts like an interface elements between the superstructure and the underlying soil or rock. It is well understood that engineering structures despite being constructed with adequate health and safety measures do fail or collapse.
Also Read: Deep Foundation – Types – Uses – Advantages – PDF
The failure of structures can be a collapse or performance failures. The performance failures are less life threatening but are more meaningful to discuss. According to American Society of Civil Engineers, “the failure” is an unacceptable difference between the expected and observed performance.
The failure of foundation may be due to poor design, faulty construction, and overloads. The causes of foundation failures are:
- Construction error
- Improper soil investigation
- Fluctuation of ground water table
- Seismic loads
Types of foundation failures
Drag down & Heave
Heaving is a leading cause of foundation failures on expansive and compressible soils. In case of foundation on a compressible soil there is always a chance of foundation failure by drag down and heave. In plastic soils, the draw down or settlement is accompanied with heave as well. Because of this there is a differential settlement that causes support failure of the foundation.
Similarly in case of expansive soil, the swelling and shrinkage due to hot dry wind and intense heat can lead to foundation settlement. Sometimes, uneven saturation of expansive soils can also cause heave due to expansion and contraction after drying.

Similar problem of heave and contraction is observed when foundation is placed in extremely cold condition (below freezing point). Moisture present in soil expands approximately 10% upon freezing causing differential settlement and soil pressure of the order of 2 Mpa. Controlling ice expansion is impractical.
How to prevent?
In cold areas the ice adhesion and uplift can be avoided by using granular backfill around foundation walls of footing pedestals. Along with insulation you can reduce the depth of the foundation or the amount of the frost heave.
The best technique to construct foundation on expansive soil is by soil stabilization. Stabilization with lime, lime-fly ash, Portland cement, and bituminous materials is very popular. You can prevent soil heaving by providing rain gutters to collect water from roof. Arrangements must be constructed to control moisture or rain water from entering into the foundation soil. The possible remedial measure is by underpinning with piers.
Lateral Movements & Loads
Lateral loads are very critical and catastrophic because in such cases, without lateral support, there are grave chances of structure collapse. The lateral loads in soil are possible when there is a removal of existing side support adjacent to a building or when there is excessive overburden on backfill or retaining wall. Lateral movement is also observed during earthquake when structure fails due to lateral movement of soil beneath the foundation following liquefaction.
How to prevent?
There is no remedy for such failures but definitely preventive measures in terms of “supported excavation system” for “deep excavation problems” can be adopted to avoid such failures. It is therefore recommended to follow proper planning of subsurface investigation before excavation. Analysis and design along with construction control and supervision can prevent foundation failures due to lateral movement & loads.
Load Transfer Failures
We know that foundation is meant to transfer load from superstructure (over the ground) to substructure (under the ground) on a larger area. It converts the concentrated loads and spreads it over an area with a magnitude that is way less than the bearing power of the soil.
In geotechnical design of foundation, we estimate and predict the bearing capacity of soil. This bearing capacity is uncertain and there is a possibility that the foundation is inadequate to take the load from superstructure and failure.
To account for such uncertainties, geotechnical engineers use a factor of safety. In this way the uncertainties like natural heterogeneity or inherent variability or measurement error and model transformation uncertainty is taken care of.
Vibrating Effects
What do you think might be the condition of your house foundation if there is a nearby blasting going on? Obviously these vibration effects because of blasting, pile driving, dynamic compaction of loose soil, operation of heavy construction and similar activities can induce ground and structure vibrations that can cause foundation failure.
As a result of such ground structural vibrations, there can be dynamic settlement in soil due to densification and liquefaction. It is therefore recommended to monitor and control ground and structure vibrations to mitigate such ground settlement hazards.
Floating & Water Level Changes
From our geotechnical engineering classes, we know that the soil behavior considerably changes upon rising and falling of ground water levels. Rise in water level reduces the bearing capacity of the fall while on the other side the lower of ground water level causes ground subsidence or formation of sinkholes due to increased overburden effective stress value.
Due to heavy rain and seepage flow the ground water level can go up while because of uncontrolled pumping or dewatering during construction of deep basement the same can go low.
Another phenomenon of increased water usage is formation of sinkholes. The majority of cases related to formation of sinkholes are associated with collapsible soils.
To avoid destruction of property and the contamination of groundwater, it is important to monitor potential sinkhole formation and control on dewatering and ground water level.
Design & Construction Errors
Another common cause of foundation failure is because of improper design and construction planning. Errors relating to temporary shoring, bracing, and protection works during construction can lead to foundation failure. A classic example is when you excavate deeply near a tall building there is always a chance of foundation failure.
To prevent such a failure you can adopt soil nailing which is a latest and most widely used technique for supporting the vertical excavation. You can prevent unstable natural soil slopes to collapse by using soil nailing technique.
Earthquakes
Some engineers believe that earthquake only damages the walls or roofs of the buildings. But actually the violent shaking of an earthquake is capable of damaging drastically the foundation of any manmade structures. Due to earth’s sudden movement the foundation of the building moves with the ground and the superstructure and its contents shake and vibrate in an irregular manner due to the inertia of their masses.
The earthquake can lead to certain instabilities and failures below the ground that can cause foundation failures. The vibrations transmitted from the ground to structure, differential settlement, lateral spreading, landslides, ground failure, and instabilities; all are the outcomes of a seismic activity.
Soil liquefaction is also a result of earthquakes. In this phenomenon the saturated soil substantially loses strength and stiffness in response to an applied stress usually earthquake shaking or other sudden change in stress condition, causing it to behave like a liquid. The soil loses its ability to resist shear and flows much like quick sand. Anything relying on the substrate for support can shift, tilt, or rupture, or collapse.
Uplift Forces
Generally the foundation is subjected to three types of loads, i.e., the downward force (compression), the uplift (tension) and the horizontal shear. One of the major causes of foundation failure due to uplift is presence of expansive soil beneath the foundation. Expansive soils pose a significant hazard to foundations for light buildings.
Slope Instability & landslides
There is always a chance of foundation failures when it rests on an unstable slope or if there is a landslide. The slope instability can be because of reasons like steep slope, rapid movement of landmass due to landslide, groundwater table changes, heavy rainfall, earthquake and other vibrations, removal of the toe of a slope or loading, etc.
The resistance to a landslide or slope instability is offered by the type of soil and the geometry of the slope. Preventive and remedial measures include modifying the geometry of the slope, controlling the groundwater; constructing tie backs, spreading rock nets, providing proper drainage system, provision of retaining walls, etc.
Case Study of Foundation Failure
Leaning Tower of Pisa
One of the most famous and well-known foundation failures is that of Leaning Tower of Pisa which a failure turned fame is. It is rather only case where a foundation failure didn’t completely ruin the building. The structure was built 840 years ago but was stopped after soil-related foundation issues. Later on in 1272 the foundation repair work carried out but still the tower continues to its downward descent but a slow pace.

Ocean Tower in Texas
Another famous foundation failure is a 31-story building – South Padre Island’s Ocean Tower in Texas. In early 2008 a foundation problem was discovered and the building was never completed. Because of the expansive soil underneath the foundation the tower began to sink and lean. Ultimately, the tower had to be demolished in 2009.
Foundation Failure in China
In June 27, 2009, a 13-storey building in Shanghai China meant for flats, still under construction, tipped over on one side killing one person due to foundation failure. According to official reports the causes of failure was an underground garage that was dug for about 4.6 meters on one side while on the other side the excavated dirt was piled on to a height of 10 meters. This resulted in a lateral pressure of 3,000 tonnes which was greater than the pile foundation capacity of the structure.
That’s not Yet Over
Here is an amazing video I’ve made for “5 Famous Foundation Failures in Construction” don’t forget to watch it and subscribe it.
[su_youtube url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HYAVrbhXZvs” width=”460″ autoplay=”yes”]
[su_box title=”Don’t Forget to Subscribe to Our Channel” style=”glass” box_color=”#f64420″]Are you willing to stay tuned to a whole lot of fun and information related to construction and civil engineering? if Yes than what you’re waiting for? Just hit this subscribe button and stay updated when it matters the most :
[su_button url=”https://youtube.com/c/saadiqbalengr/” target=”blank” style=”soft” background=”#c74740″ size=”7″ center=”yes” icon=”icon: youtube”]Subscribe Now[/su_button]
[/su_box]