Different types of field density test are being practiced in different parts of the world for evaluation of in-situ soil compaction and knowing the relative degree of compaction.
FDT is an acronym of Field Density Test that is an in-situ Quality Control test carried out at site for knowing the increased density or compaction achieved at site on the different types of embankments and fills.
It is carried out by Laboratory persons of Contractor under the supervision of QC team from the Consultant after completion of the required number of passes by compactor / roller determined in test fills at site.
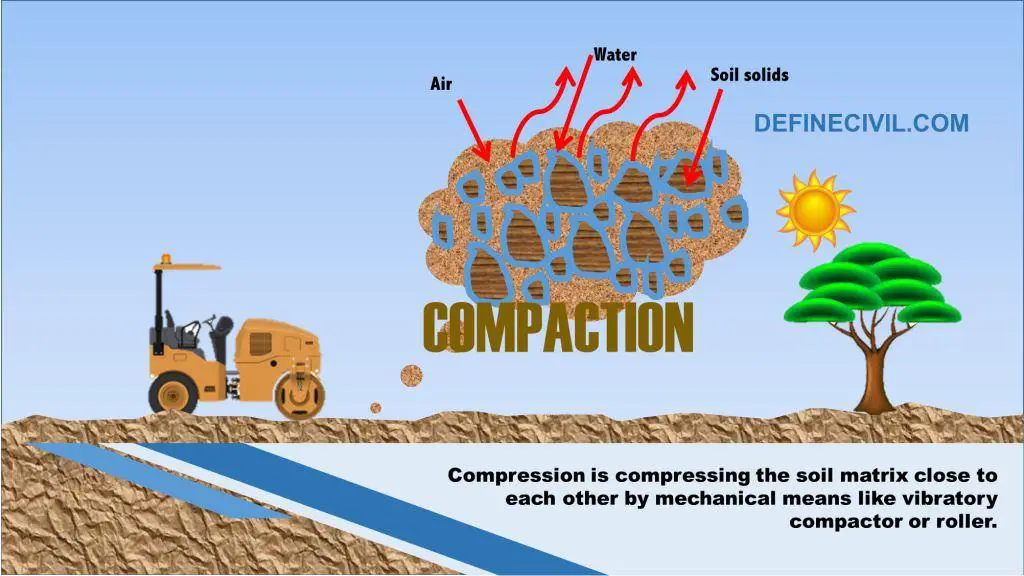
What is compaction?
Compaction of the soil means pressing the soil particles close to each other by mechanical methods. Air present in the void spaces are expelled from the soil mass as a result of compaction and therefore the density is increased.
The compaction and its testing by field density test are very important and repetitive steps during earthwork phases of construction in a project. In case of flexible pavement, improper compaction of subgrade can cause pavement failures like rutting, potholes, or settlement cracks.
The compaction of the soil generally increases the shear strength of the soil, and hence the stability and bearing capacity. It is also useful in reducing the compressibility and permeability of the soil mass.
Whether you are constructing a building, multistory plazas, highways / pavements or even in Dam or hydropower projects you have to know the basic knowledge of fdt
Whether you are a quality control engineer or site engineer from Contractor or from supervision team there are a lot of factors that must be known for ensuring the quality and sustainability of the structure.
Types of FDT Tests
The following are the most common types of field density test:-
- Sand Replacement Method or Sand Cone Method
- Core Cutter method
- Water Replacement Method
- Rubber Balloon Method
- Heavy oil Method
- Nuclear Moisture Density Meter
The compaction or increase in density is achieved at site with the help of Tampers, different types of roller like steel drum roller, pneumatic-tyred roller, sheep foot rollers or different types of vibratory compactors.
In some advance scenarios where above methods won’t work; the engineer can demand the use of compaction piles, precompaction method, compaction by explosives, compaction by pounding or terra probe method.

Discussing all of the above methods is actually out of the scope of this post. In today’s article my main focus would be on the different types of fdt methods enlisted above.
I would be answering questions like what method is suitable for particular type of soil. Which test is more economical and easy to perform? Which fdt test method give more accurate result?
So let’s dive in.
In one of my previous article I have already explained the field density test calculations that are performed after carrying out the tests. In that post I have discussed about the sand cone method and core cutter method.
These two methods are actually the most common of all. I have worked for many mega projects in all of them we are either using sand replacement or core cutter.
From these two methods, sand replacement is even more common even to such an extent that whenever you talk in the field about FDT you are assumed to refer sand replacement method.
DID YOU KNOW?
Have you ever seen someone performing FDT on the concrete?
I have not seen but I actually have performed this test myself. What?
Yeah! If you haven’t work on the Dam or Hydropower project which has mass concrete structures you might not know about roller compacted concrete.
Roller compacted concrete is actually a hard slump low strength concrete that is poured in layers and compacted by vibratory rollers. This is low permeable concrete that is usually used around the banks of water reservoirs.
In this concrete the compaction is also tested by fdt usually sand replacement method.
Also Read: Compaction of Concrete – Importance – Under – Over vibration – PDF
What is FDD test?
FDD or Field Dry Density Test is a field quality test to evaluate dry density of soil by dividing wet density of soil by the water content in percent. The compaction in percentage at site is determined by dividing the dry density of soil with MDD or maximum dry density from proctor test.
Now that you know about the FDD and FDT acronym. Do you know what is MDD or MWD? I’m just asking this because these two are also relevant to this subject. Well, MDD is for Maximum dry Density while MWD is maximum wet density.
What is MDD of soil?
MDD is the density that is achieved in the laboratory at the optimum moisture content (OMC). It is the maximum density you can achieve for given conditions. So, quality control officers use this as a threshold value to determine if the pavement or earthwork is of good quality or not.
Field Density Test Apparatus
FDT test apparatus include a sand pouring conical cylinder or jar that has a pouring cone at its base. The base has a hole of diameter in coherence with conical funnel. It has a metal valve or shutter while the cone is used to fill with the soil. It is important to calibrate the apparatus for determining the unit weight of sand.
The above apparatus is used for determine field density test by sand cone method. For other tests methods like water-replacement or rubber-balloon method; you need to follow relevant test apparatus.
FDT Test requirement
FDT test is required for all structures that are to be founded on ground or soil. Projects like road construction, building foundation, sewerage line, water-supply line, embankment making, dam construction, culvert, and trench construction.
Frequency of FDD Test
Well as per the IS code 2720 Part-28 here are some of the recommendations for frequency of tests and permissible limits.
Frequency of test
- For embankment – 1 test per 1000 m2 area
- For granular sub base – 1 test per 500 m2 area
Permissible limits for different reaches
For permissible limit here are recommended values:
- for embankment – minimum 95%
- For subgrade – minimum 97%
- For granular sub base – minimum 98%
FDT Test Procedure
The procedure followed for field density test is generally as follows:-
- The surface of the soil is leveled and brush is used to clean the surface from fines.
- The apparatus of field density is used to get the sample of soil for bulk weight using physical balance. In core cutter it is obtained from the soil in the core while in sand replacement, the soil on the flat tray is weighed.
- After knowing the weight of the soil, the next step is to determine the volume of the hole or that of the soil. In sand replacement or rubber balloon method it is measured indirectly while in core cutter method you can calculate the volume of core.
- The weight is divided by volume to determine the in-situ bulk density of the sample.
- A representative sample of the soil is taken for determination of moisture content in the filed or at site by speedy moisture test.
- After knowing the moisture content the dry density of the soil is determined using following formula.
- Dry density = (1 + bulk density / moisture content)
- Now you know the field dry density or in-situ dry density and that is afterwards compared with the maximum dry density (MDD) obtained already from the Proctor test or modified proctor test.
- Water replacement method for field density
Also Read: Rigid Pavement- Difference between Rigid vs Flexible Pavement
Comparison of Different Methods
The following points include the draw backs, benefits, pros and cons of different methods of FDT and they will help you in judging the efficacy and usability of the method in your case at site.
- The core cutter method is actually well suited for soft soils like clay soils or other cohesive soils that are placed as fills. This method cannot be used for coarse grained soil as the core cutter would not penetrate through them due to high resistance at the tip of the instrument.
- In comparison to core cutter method, sand replacement method or sand cone method is known to be better as it can be used in different types of soils and the results obtained are also much more appropriate. The main difference between sand replacement method and core cutter method is the procedure. In core cutter method you use a core and volume is used as that of the core. While for sand replacement the volume is obtained indirectly by using a calibrated sand.
- However Sand replacement method the calculation is lengthy as it involves many steps and you need more area of the reach to test. It also tend to be less accurate than nuclear density gauge, which is very costly but is more accurate.
- The rubber – balloon method although can get large samples, direct readings are obtained but it is little awkward method that is slow and can be abandoned easily in case of balloon breakage.
- Nuclear density test is the fastest of all the methods and is easiest to redo when needed. You can get more tests for statistical reliability.
- However, in case of nuclear density test you won’t be able to get any sample and it involves radiation which may be harmful and damaging to the operator of the instrument if suitable precautions are not taken in to account.
- Nuclear density test cannot be used if rocks are in the path and it can lead to ambiguous results if miscalibrated.
FDT Meaning in Construction
FDT is an acronym for Field Density Test. FDT is a in-situ density test of soil that is used in various types of construction works like highways, DAM construction, Embankment filling, and backfilling in order to access the quality of density achieved at site. FDT like many other tests on soil in civil engineering is a quality control tests. Other tests like CBR, Proctor Test, Moisture Test, Vane Shear Strength Test etc. are also carried out to access different parameters of soil.
The density we obtain as a result is called in situ dry density of the soil. So, if anyone asks you about which of the methods is used to find in situ density of soil, the answer would be simply – the sand cone method.
Experts call this as in-situ density because it is measured at the field with actual depth of the soil. You are measuring the weight of the excavate material and then divide it with the in-situ volume of the hole. Generally when you determine the density, it is the bulk density i.e. the density with actual moisture condition. So, after obtaining the moisture content we determine the dry density.
FAQs
Here’re some of the FAQs about these methods:
- What is Field Density test definition?
Field density test is an in-situ test that is used to evaluate the compaction achieved at site.
- What are the different methods of field density test?
The different methods are: Core cutter method, Sand replacement method, rubber-balloon method, nuclear density test, and water replacement method.
- What is FDT meaning in construction?
FDT is a short form of Field Density test or Field dry density test. This test method is used to evaluate the compaction of soil achieved at site in comparison to the maximum dry density achieved in laboratory by standard proctor test.
- Which method is best for FDT on roads?
For FDT on roads, sand replacement is mostly used for subgrade, sub-base and base.
- What is the purpose of field density test?
FDT is a field quality control test that is used to determine if the reach or soil layer in road pavement is compacted as per the requirement of the project or not. In most projects, 95-98% of Maximum dry density is taken as criteria to pass a layer of compacted soil.
How is FDT test conducted?
We can summarize the steps for fdt by sand replacement as: Dig a hole in the ground and weigh the excavated soil from the hole. Pour calibrated Sand in the apparatus and weigh whole of the apparatus. Now pour the sand in the hole and weigh again. Subtract the weight to get the reading of the soil needed to fill the hole. Now using calibrated weight conversion, calculate the volume of hole. Divide the weigh of the excavated soil from the volume of hole to get the bulk density of the soil.
- What is the most accurate method to determine field density test?
If we compare all the methods of field density test, the most accurate method is Field density by Nuclear density gauge. If we compare method of sand replacement and core cutter, core cutter method is more accurate but it can only be used in clayey soils.
Final Words…..?
Actually different projects have different requirements so selecting the type of test is a very important step that can be very tricky if you don’t know the different types of tests or their pros and cons.
So I have tried to cover all the tests that are practiced as in-situ dry density test and while I am writing the article I have searched a lot but was not able to find some article so I thought it would be very helpful for ones like me.
So while I am publishing the article I would be preparing an infographic that would surely help you in remembering the different methods so wait for that and stay tuned with definecivil.com.
So If this article has helped you please don’t forget to share it with your friends.


















