M25 concrete is a type of concrete mix that is designed to produce concrete with a characteristic compressive strength of 25 megapascals (MPa) at 28 days after it has been placed. It is often used for high-strength applications such as foundations, beams, and columns in high-rise buildings.
Concrete Mix Design – General discussion
Mix design refers to the process of determining the proportions of concrete ingredients, including water, cement, fine aggregate (such as sand), and coarse aggregate (such as gravel or crushed stone), to achieve the desired strength, durability, and other characteristics of the finished product.
The mix design process typically involves selecting appropriate materials and determining the proportions of these materials based on the specific requirements of the project.
Also Read: Harsh mix of concrete – Harshness in Concrete is due to
Factors that may be considered in the mix design process include the type and strength of the concrete required, the intended use of the concrete, the exposure conditions (such as the presence of moisture or extreme temperatures), and the availability of materials.
Once the materials and proportions have been determined, the mix design may also include testing to ensure that the resulting concrete meets the desired specifications.
This may involve performing laboratory tests such as compressive strength testing or field testing to assess the performance of the concrete under real-world conditions.
Mix design is an important aspect of concrete construction, as the properties of the concrete can have a significant impact on the performance and durability of the finished structure. It is typically performed by a structural engineer or other professional with expertise in concrete design and construction.
Technical details regarding mix design:
Material properties:
Information on the properties of the various materials used in the mix, such as the specific gravity, absorption, and particle size distribution of aggregates, and the strength and chemical properties of cement.
Proportions:
The specific proportions of each ingredient in the mix, including the water-cement ratio, the volume of aggregate, and the proportions of fine and coarse aggregate.
Mixing instructions:
Detailed instructions on how to mix the ingredients to produce the desired concrete, including the order in which the materials should be added, the mixing time and speed, and any other special considerations.
Also read: How to correctly fill wide cracks in concrete?
Testing procedures:
Information on the laboratory and field tests that should be performed to ensure that the concrete meets the desired specifications, including details on test equipment, sample preparation, and test procedures.
Performance data:
Data on the performance of the concrete under different conditions, including information on the compressive strength, flexural strength, and other properties of the concrete.
Quality control procedures:
Procedures and guidelines for ensuring the quality of the concrete during the mixing, transporting, and placing processes, including details on sampling, testing, and record-keeping.
Also Read: Concrete Block Calculator – How many blocks you need?
Types of mix ratios:
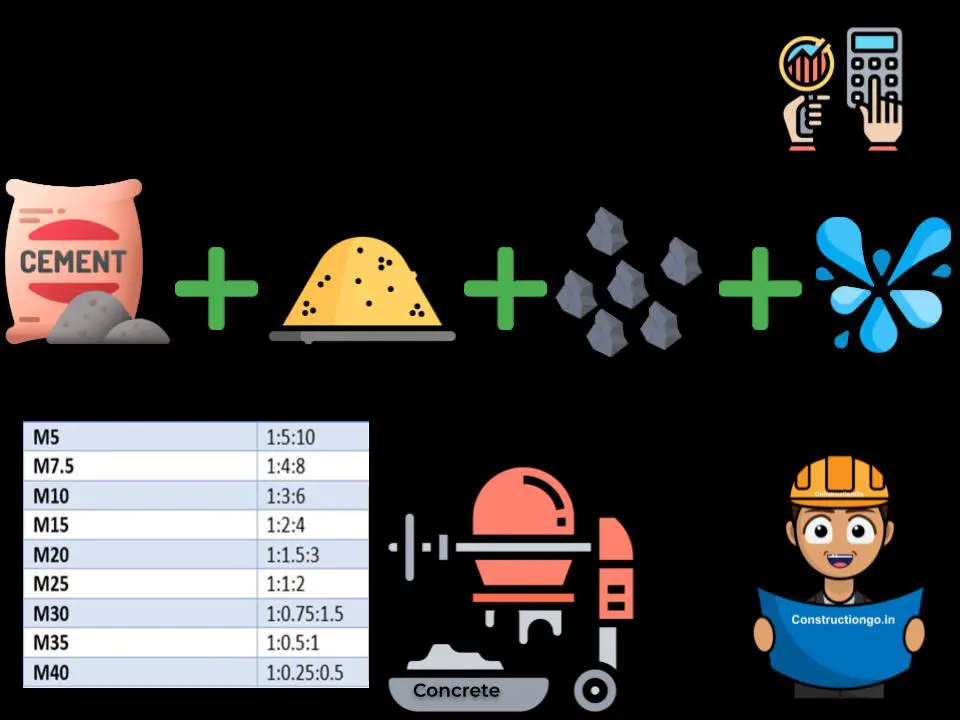
There are many different types of mix ratios that can be used for concrete, depending on the specific requirements of the project and the desired properties of the finished concrete. Some common types of mix ratios include:
- Nominal mix ratio: This type of mix ratio is based on approximate or “nominal” values, rather than on the actual characteristics of the materials used. Nominal mix ratios are often used for simple construction projects where the concrete does not need to have high strength or durability.
- Standard mix ratio: This type of mix ratio is based on the properties of the specific materials used and is designed to produce concrete with specific strength and durability characteristics. Standard mix ratios are often used for more complex construction projects or for applications where the concrete needs to have specific performance characteristics.
- Design mix ratio: This type of mix ratio is based on a detailed mix design process that considers the specific requirements of the project and the desired properties of the finished concrete. Design mix ratios are used for high-strength or structural applications and are typically developed by a structural engineer or other professional with expertise in concrete design.
- Maximum density mix ratio: This type of mix ratio is designed to produce concrete with the highest possible density, which can be useful for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in the foundations of high-rise buildings.
- Minimum cement content mix ratio: This type of mix ratio is designed to use the minimum amount of cement necessary to produce concrete with the desired strength and durability characteristics. This can be useful for reducing the cost of the concrete or for reducing the environmental impact of the construction project.
The specific mix ratio used in a project will depend on the type and strength of the concrete required, the intended use of the concrete, the exposure conditions, and the availability of materials. It is important to choose the appropriate mix ratio to ensure that the finished concrete meets the desired specifications and performs as intended.
M25 Concrete mix calculator
This calculator allows you to enter volume of concrete and it will show the quantity of cement sand and aggregating corresponding to the mix design of M25 i.e. 1:1:2.
Enter the volume of concrete in m3:
For m3 of concrete, you will need:
Cement: m3
Sand: m3
Aggregate: m3
M25 Mix Ratio concrete:
The mix ratio for M25 concrete is typically expressed in terms of the proportions of cement, water, fine aggregate (such as sand), and coarse aggregate (such as gravel or crushed stone) used in the mix. A common mix ratio for M25 concrete is 1:1:2, which refers to a mix that contains 1 part cement, 1 part fine aggregate, and 2 parts coarse aggregate by volume. This mix ratio is based on a nominal mix design, which means that it is based on approximate or “nominal” values, rather than on the actual properties of the materials used.
The strength of M25 concrete is achieved through a combination of the cement, water, and aggregate used in the mix, as well as the mixing, placing, and curing methods used. The specific mix design and production methods will depend on the specific requirements of the project and the desired properties of the finished concrete. Some advantages of using M25 concrete include:
High strength:
M25 concrete h a high compressive strength, making it well-suited for applications that require strong, durable concrete.
Good workability:
M25 concrete has good workability, making it easy to mix, transport, and place. This can reduce construction costs and improve efficiency.
Low shrinkage:
M25 concrete has low shrinkage, which can help to reduce cracking and other defects in the finished concrete.
High durability:
M25 concrete has high durability and can withstand harsh weather conditions and other types of exposure. This can help to extend the service life of the concrete.
Versatility:
M25 concrete can be used for a wide range of construction applications, including high-rise buildings, bridges, industrial structures, and infrastructure projects.
M25 concrete mix ratio cement
M25 refers to a concrete mix with a compressive strength of 25 MPa (megapascals) after 28 days. Here is the general mix design for M25 grade concrete:
- Cement: 300-325 kg/m^3
- Fine aggregate (sand): 600-675 kg/m^3
- Coarse aggregate: 975-1050 kg/m^3
- Water: 150-175 kg/m^3
- Admixture: 0-5% by weight of cement (optional)
In an M25 mix, the cement content is typically around 10-12% of the total concrete volume. The mix ratio of M25 concrete in terms of cement:sand:aggregate is usually 1:1:2. This means that for every 1 part of cement, there are 1 part of sand and 2 parts of coarse aggregate in the mix.
Also Read: Can You Pour Concrete Over Concrete? – Level – Thickness
Applications and Uses of M25
Here is a table for the M25 mix ratio of concrete specifying different uses:
| Use | Cement (kg) | Fine Aggregate (kg) | Coarse Aggregate (kg) | Water (kg) |
| Foundation | 312.5 | 625 | 937.5 | 187.5 |
| Columns | 312.5 | 625 | 937.5 | 187.5 |
| Beams | 350 | 700 | 1050 | 175 |
| Slabs | 337.5 | 675 | 1012.5 | 162.5 |
| Footings | 337.5 | 675 | 1012.5 | 162.5 |
Advantages:
In addition to its high strength, M25 concrete may also have other desirable properties such as good workability, low shrinkage, and high durability. These properties can make it well-suited for a variety of construction applications, including:
M25 concrete is often used for the foundations, beams, and columns of high-rise buildings, due to its high strength and ability to support the weight of the structure.
M25 concrete may be used for the construction of bridge decks, piers, and other structural components due to its high strength and durability.
M25 concrete may be used for the construction of industrial structures such as factories, warehouses, and storage facilities, due to its high strength and ability to withstand heavy loads.
M25 concrete may be used for the construction of roads, highways, and other infrastructure projects due to its high strength and durability.















