Among many different types of foundation for structures, deep foundation comes handy in number of ways. Deep foundation transfers the structure loading to the earth farther down. Be it a bridge, a building, or a commercial plaza; deep foundation helps in transferring the loading to high bearing strata several meters down the soil.
In order for the foundation to be a deep foundation, it has to go beyond 10 feet. Moreover, the depth to width ratio is larger than 4 to 5. In other words, we can say that deep foundation has depth greater than its width.
Introduction to deep foundation
Following are the most obvious scenarios to opt deep foundation:
- The loading is too heavy including all types like dead, live, or imposed load.
- Or the bearing capacity of soil just beneath the probable depth of foundation is not enough to support the building load.
- Offshore construction in marshy areas
- Where a structure is susceptible to uneven settlements.
For heavy traffic bridges spanning several feet; the foundation has to be always a deep foundation. But in case of buildings; you can’t say for sure. For residential buildings mostly 1 or 2 stories; a shallow foundation serves the purpose. However, for a commercial multistory buildings or skyscrapers; we need to provide deep foundation.
Apart from loading or structure type; the geo-engineers will evaluate the type of soil. So, it is pretty obvious that shallow foundation is not good for expansive or clayey soils.
Anyhow, the deep foundation is more expensive than shallow foundation as the construction process is complex. But it is a feasible solution as you can’t always improve the engineering properties of soil to increase bearing capacity or shear strength.
Type of deep foundation
Apart from pile foundation, other types of deep foundation include; pier, shafts, caissons, cylinder, and basement foundation.

Pile Foundation
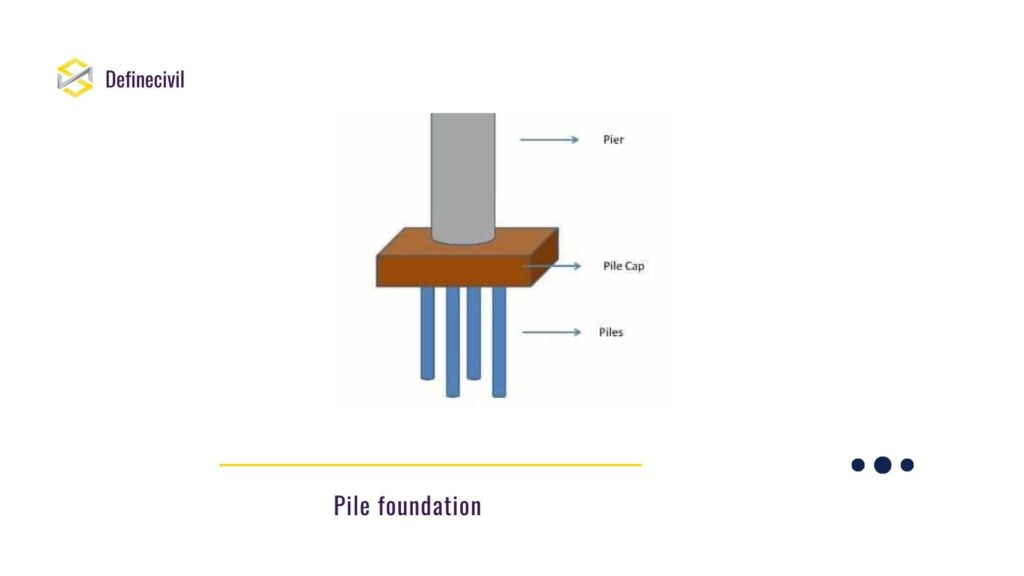
Pile foundation is the feasible solution in most of the cases. It is a most common type of deep foundation. We either drive precast pile or make in-situ piles. But obviously, the geotechnical engineer will judge the feasible solution.
A pile foundation comprises of long-cylindrical columns that transfer the load by end-bearing or surface friction of stem to the high dense or soils of high bearing capacity. A common example of its usage is in flyover or a bridge. It takes the loading from the bridge pier through a pile cap and transfer the loading to the rocky soil beneath.
A pile can be of materials like reinforced concrete, wood, steel, or timber. Steel or timber piles are usually precast driven piles. We use to drive them into the soil with a hammering action. Reinforced concrete piles are suitable for cast in-situ cases.
Types of pile foundation
The classification of pile foundation based on loading mechanism includes:
- End Bearing Pile – As the name implies, this type of pile foundation takes loading only at the bottom of the shaft. It vertically transfers the loading directly to the high bearing strata underneath. We prefer this type of pile foundation for soft or hard soils but the depth is less than 40 meters. All driven piles are end-bearing piles.
- Friction Pile – When the loading is excessive and the end-bearing piles can fail, friction piles are preferred. They take loading as a result of skin friction of the pile and the adjacent soil. Anyhow, we only prefer friction pile when depth of high bearing strata is beyond 40 meters.
- Anchor Pile – Anchor pile are a type of tension piles that transfers loading either by ground friction and under-reaming or by bonding into un-fractured rock.
Caisson or well foundation
If you’re still unsure how underground structures are built, the concept of caisson or well foundation will be very fascinating for you. For the excavation of foundation for bridges, piers, and dock structures in rivers or water-bodies; we use caisson or well foundation to establish a dry working area for construction.
Well or caisson foundation is either made by wood, steel, or RCC. Anyhow, stability of foundation is an important concern in this type. The Construction of caisson foundation is pretty complex and thus only skilled manpower is used. .
Pier Foundation
As the name implies, a pier foundation involves use of a column-type shaft or cylinder that supports and transfers large super-imposed loads to the firm strata below. You’ll notice a pier foundation if your pass a flyover or an interchange. All the bridges or flyovers have piers supporting the girders of ramps. A pier is generally large in diameter than a typical column.
Read More: Pier Foundation- Types – Uses
Masonry
Anyhow, the size depends a lot on the type of loading and the subsurface soil bearing capacity. A pier can be of concrete or masonry structure. We prefer masonry pier foundation when we have hard strata at shallow depth. Anyhow, you can only extend the pier foundation upto 4 to 5 meters. As going deeper than 5 meters will make masonry pier construction challenging.
Concrete piers
Concrete piers are round, square, or rectangular shaped columns that are most common for supporting heavy loads. They’re large in size but are used for deeper piers.
Drilled Caissons
Drilled pier or drilled caissons are another type of pier foundation. They typically take axial loadings just like a column. But unlike masonry or concrete piers, they can go even deeper. However, mechanical excavation methods are used to drill piers.
Also Read: Caisson Foundation – Types- Box – Open- Bell
Advantages of deep foundation
Although you can’t decide a type of footing merely on the basis of advantages or disadvantages; but still it’s handy to know them.
Deep foundations are best in terms of taking heavy loadings. They’re able to sustain the high failure loads and there’re no such things as displacements or settlement.
Only because of deep foundations, we’re able to construct high-rise skyscrapers and shopping centers on areas of low-bearing soils.
Deep foundations are also good at resisting the seismic loading that are not the case otherwise with shallow foundations.
Disadvantages
It is without a doubt that deep foundations are difficult to construct. You need highly skilled manpower and machinery. Pile foundation need auger boring or percussion boring and both the methods are highly technical. They need experienced contractors and have more chances of mistakes.
You need to have high budget for your project. In fact, the cost of deep foundation is almost 2 or 3 times the cost of shallow foundation. Moreover, the safety factor is also critical. Its construction involves risky maneuvers and so you’ve got to hire a pretty smart safety inspector.
Shallow vs deep foundation
Shallow foundations like isolated pad footing, raft footing, or strip foundation are best for smaller or light-weight buildings. They’re used only on high quality or highly dense soils where settlement is not a big concern. They’re only a few feet deep into the soil. A deep foundation on the other hand, can go as deep as several hundred feet. I’ve personally observed deep foundations more than 300 feet.
















