A mat foundation is defined as a thick reinforced concrete slab that spreads over a large area of soil and transfers loads to the underneath soil. It supports all the columns and load bearing walls of a structure. A Mat foundation covers the entire footprint of a building. It is also commonly known as Raft foundation as it spreads over soil like a raft. It is a type of shallow foundation.
We prefer mat foundation in low-bearing soils for residential buildings and where loading conditions are not severe. The best part of mat foundation is its ability to prevent differential settlement that’s a critical problem in isolated foundation. This type of shallow foundation reduces the stress on the particular section of soil. It helps distribute the load equally on the entire mat slab.
Also Read: 5 Types of footing -Best footing – Images- Uses [PDF]
Mat foundation takes area loading. So, if you have a particular weight on the mat; we can determine the stresses by dividing the load on the unit area of slab. For example, if your foundation measures 10 meters in length and 7 meters in width, the self-weight of the slab will be 1.86 tons per meter square.

When to use mat foundation?
Mat foundations are considered if:
- The structural loads are so high or soil conditions are so poor that spread footings would be exceptionally large. As a general rule of thumb, if spread footings would cover more than 50% of the building footprint area, a mat foundation will be more economical.
- If the soil is very erratic and prone to excessive differential settlements (heaves). The structural continuity and flexural strength of a mat will bridge these irregularities.
- The uplift loads are larger than spread footings can accommodate. The greater weight and continuity of a mat may provide sufficient resistance.
- The bottom of the structure is located below ground water table, so water proofing is an important concern. Because mats are monolithic, they are much easier to waterproof.
- The weight of the mat also helps to resist hydrostatic uplift forces from groundwater, thus making it useful in areas where footings are often prone to rising water table.
Types of Mat Foundation
There are certain types of mat foundations that are used depending on design considerations.
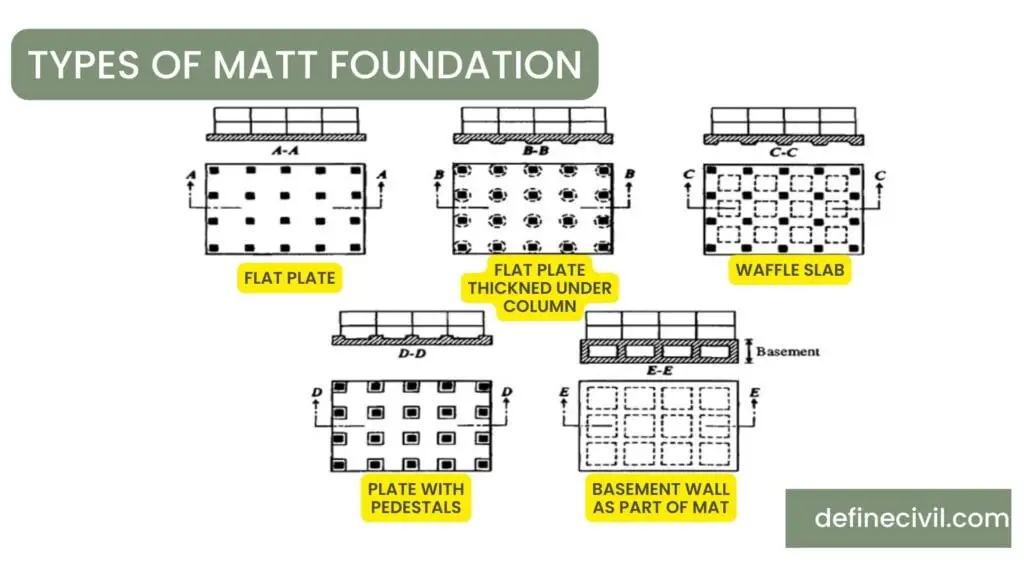
Flat Plate
This type of mat foundation is used for fairly small and uniform spacing of columns and when the supporting soil is not too compressible. It simply consists of a mat slab that is supporting columns over it.
Flat Plate Thickened under Columns
In this type of foundation, areas where columns join the mat slab have more thickness with respect to rest of the slab. This is used for columns with heavy loads which may require large shear strength or flexural strength of slab.
Beam and Slab
In beam and slab mat foundation, beams are constructed along with mat slab. These beams run in perpendicular direction and are jointed to the slab. The columns are situated at the intersections of beams. This foundation is used for large column spacing and unequal column loads.
Flat Plate with Pedestals
A pedestal is essentially a compression member which is provided to carry loads from columns to footings below the ground. In this type of foundation, pedestals are constructed at points where columns will join the mat slab.
Then columns are constructed over these pedestals and load is transferred to the slab. It is used for compensated foundations to avoid differential settlements in weak soils.
Combined Pile Mat Foundation (CPRF)
In this type of foundation, piles are provided below the mat slab. The piles support the mat foundation. This type of foundation is preferred when the soil underneath is highly compressible such that the chances of settlement are very high.
Also, when the water table is high this type of foundation is useful. In this type of foundation the ultimate load carrying capacity is greater.
Cellular Mat Foundation
Also known as box type mat foundation. In cellular mat foundation, box like structures are constructed which are connected by slab both at the top and bottom. The walls of these box structures behave like beams. These walls act as stiffening elements.
The columns are then constructed above these boxes. This foundation is useful for loose soils and when the structure is subject to high bending stresses.
The Concept of Floating Foundation
Mat foundations are often placed in deep excavations. This approach has certain benefits. Firstly, it provides underground space. Secondly, this design decreases bearing pressure because the weight of the foundation is substantially less than the weight of soil excavated.
In other words, the weight of structure and foundation is partially offset by the removal of soil from excavation. This reduction in bearing pressure significantly reduces settlement. This approach is particularly useful while designing mat foundation on soft soils.
Also Read: Pros and Cons of Floating Building
Construction of mat foundation
If you’re looking to have a mat foundation for your home, here’re some important measures that will prevent you from losing money:
- As the foundations rests directly on the soil, make sure you have a water proof membrane sheet on the top of the ground surface. Otherwise, the water of concrete will seep into the underneath ground lowering the compressive strength of concrete.
- For mat foundation, we use low slump concrete and we make sure to have proper compaction in terms of poker vibrators.
Also Read: Compaction of Concrete – Importance – Under – Over vibration – PDF
- Reinforcement mesh needs suitable cover to avoid rusting later on.
- Make sure to compact the underneath ground with vibratory compactor and carry out FDT if possible to evaluate the field compaction.
- Curing of concrete is also an important quality control aspect. We mostly cure mat foundation concrete by ponding method of curing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mat Foundation
Advantages
- Mat foundation is well suited for expansive soils as its homogeneity can counter the swelling and shrinking action of such soils.
- Mat foundation offers good resistance against differential settlement.
- Mat foundation is useful at places where it is necessary to provide shallow foundation but the soil is weak.
- Mat foundation distributes loads over a wide area.
- Mat foundation offers better waterproofing.
- Mat foundation is ideal for eccentrically loaded members.
Disadvantages
- If not treated properly, mat foundation is prone to side erosion.
- It is labor intensive and requires skilled labor.
- The cost of constructing a mat foundation is much higher.
- The design of a mat foundation is cumbersome as compared to isolated footing.
- In case of heavily loaded columns excessive reinforcement is to be provided which leads to congestion of reinforcement.















